Diplomatic Bluebook 2021
Chapter 1
International Situation in 2020 and Outlook for Japan's Diplomacy
2 Outlook for Japan's Diplomacy
In the face of major global changes and challenges, Japan must take on a greater responsibility and role than before, while collaborating with other countries. In particular, the role expected of Japan is to uphold its respect for multilateralism and take on a greater leadership role in establishing a free and fair order and rules on both the security and economic fronts, looking ahead to a post-COVID-19 world. Based on this recognition, Japan, while reinforcing its foreign policy implementation apparatus, including by bolstering Japan's missions overseas in terms of both quantity and quality, will continue to make the utmost efforts to promote its national interests and contribute to the peace and prosperity of the international community. Furthermore, Japan will further strengthen its public diplomacy to obtain understanding of and support for Japan's policies, initiatives, and positions.
(1) “Diplomacy with a Sense of Caring and Robustness”
In order to create a desirable international environment that is stable and predictable for Japan, it is important to build trust and cooperative relations with countries worldwide and the international community through diplomatic efforts, to strengthen the basis for stability and prosperity of the international community, and to prevent the emergence of threats in advance. In this respect, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs has advanced “diplomacy with a sense of caring and robustness” under the policy of “Proactive Contribution to Peace” based on the principle of international cooperation─diplomacy that respects diversity, in which Japan exerts its ability to coordinate in the international community and stands firm where a resolute response is needed.
Prime Minister Abe visited 80 countries and regions (176 countries and regions in total) since the inauguration of his second Cabinet in December 2012 until his resignation in September 2020. Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, Prime Minister Suga visited Viet Nam and Indonesia for his first overseas visit since taking office in September. Foreign Minister Motegi, since his appointment in September 2019, visited 34 countries and regions (35 countries and regions in total) and held more than 120 telephone calls and video conferences (as of January 2021). As a result, Japan's presence in the international community has steadily risen, and the personal relationships of trust between Prime Minister Suga and foreign leaders as well as between Foreign Minister Motegi and other foreign ministers have also deepened.
As a stabilizing force in the international community, Japan will continue to build relationships of trust with other countries' leaders, and while promoting its national interests, lead the international community for peace and prosperity of the world.
(2) The Seven Priority Areas of Japan's Foreign Policy
In order to protect and promote Japan's national interests, Japan will pursue diplomacy with a focus on: (1) strengthening the Japan-U.S. Alliance, the cornerstone of Japan's foreign policy and security; (2) promoting a “Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP)”; (3) diplomacy with neighboring countries, such as China, the Republic of Korea (ROK) and Russia; (4) tackling outstanding issues of concern regarding North Korea; (5) addressing the situation in the Middle East; (6) leading international efforts to create new rules; and (7) addressing global challenges.
【1 Strengthening the Japan-U.S. Alliance, the Cornerstone of Japan's Diplomacy and Security】
The Japan-U.S. Alliance is the cornerstone of Japan's diplomacy and security and plays a significant role in regional and international peace and prosperity. As the security environment surrounding Japan is becoming increasingly severe and uncertain, the Japan-U.S. Alliance is more important than ever.
With the Biden administration, which was inaugurated in January 2021, Japan will further strengthen the Japan-U.S. Alliance and will work closely to realize FOIP as well as resolve regional and international issues, including measures against COVID-19, climate change and North Korea.
With regard to the realignment of U.S. Forces in Japan, including the relocation of Marine Corps Air Station (MCAS) Futenma to Henoko and the relocation of the Marine Corps from Okinawa to Guam and other locations outside of Japan, Japan and the U.S. will continue to coordinate closely to mitigate the impact on local communities including Okinawa, while maintaining the deterrence of U.S. Forces in Japan.
【2 Promoting the vision of “Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP)”】
The Indo-Pacific region is the core of the world's vitality and supports more than half of the world's population, but is also a region which has seen complex power dynamics of countries and has experienced drastic shifts in the regional power balance. It is essential to ensure peace and prosperity in the entire region and beyond, through establishing a free and open order based on the rule of law.
From this perspective, Japan has been strategically promoting efforts to realize FOIP based on the rule of law, in cooperation with like-minded counties. This vision is now shared by the U.S., Australia, India, ASEAN and major countries in Europe, and is gaining broad support in the international community, with various consultations and cooperation under way. The significance and importance of this vision are further increasing in the transition to the post-COVID-19 era. Japan will seize opportunities for various bilateral and multilateral dialogues, including the Japan-Australia-India-U.S. dialogue, to expand the cooperation to more countries.
【3 Diplomacy with Neighboring Countries, such as China, the Republic of Korea, and Russia】
Building stable relations with neighboring countries is critical in ensuring peace and prosperity in Japan.
(China)
The relations with China, a neighboring country across the East China Sea, is one of Japan's most important bilateral relations. Stable Japan-China relations is vital for peace, stability and prosperity in the region and the international community. The relations will be further strengthened if the two countries jointly address and contribute to regional and international challenges as responsible major countries. Japan and China will continue to maintain close high-level communications, including between the leaders, to build stable bilateral relations.
At the same time, there are various outstanding issues of concern with China, and it is important that Japan continues to firmly maintain its position by taking the opportunities of high-level contacts, such as meetings between the leaders and foreign ministers, all the while strongly requesting China's concrete actions. The ongoing and strengthening attempts by China to unilaterally change the status quo in the East China Sea by force or coercion are absolutely unacceptable. With the determination to defend its territory as well as territorial sea and airspace, Japan will continue to take a calm and resolute approach to the situation while strengthening coordination with the relevant countries.
(Republic of Korea)
The Republic of Korea (ROK) is an important neighboring country, and Japan-ROK and Japan-U.S.-ROK coordination, including in dealing with North Korea, is indispensable for the stability of the region. However, the situation in 2020 and beyond has remained unacceptable to Japan due to issues, including the issue of former civilian workers from the Korean Peninsula (hereinafter referred to as “CWKs”) and the issue of comfort women. In particular, the confirmation of the judgment of the Seoul Central District Court of the ROK in the lawsuit filed by former comfort women and others in 2021 is absolutely unacceptable, as it is clearly contrary to the international law and agreements between the two countries. Based on Japan's principled positions on issues between our two countries, the Government of Japan will continue to strongly urge the ROK to take appropriate actions, including remedying the status of its breaches of international law.
(Russia)
Amidst the significant changes in the strategic environment of the Indo-Pacific, the building of stable relations with Russia contributes not only to Japan's national interests but is also extremely important for regional stability and development. There is no change to Japan's intention to place importance on its relations with Russia. On the other hand, the Northern Territories issue, which is the greatest concern between Japan and Russia, is yet to be resolved even after more than 75 years have passed since the end of World War II. Under the strong leadership of the Japanese and Russian leaders, the Government of Japan will continue to persistently negotiate with Russia to conclude a peace treaty by resolving the issue of attribution of the Four Northern Islands.
【4 Addressing Outstanding Issues of Concern regarding North Korea】
The Government of Japan has been taking various initiatives to realize its basic policy of seeking to normalize its relations with North Korea through comprehensively resolving outstanding issues of concern, such as the abductions, nuclear and missile issues, as well as settlement of the unfortunate past in accordance with the Japan-DPRK Pyongyang Declaration of 2002. Japan will continue to fully implement relevant UNSC resolutions and aim for the denuclearization of the Korean Peninsula, coordinating closely with the U.S. and the ROK, and cooperating with the international community, including China and Russia.
As well as being a critical issue concerning the sovereignty of Japan and the lives and safety of Japanese citizens, abductions by North Korea constitute a universal issue for the international community as a violation of basic human rights. Japan has positioned the resolution of the abductions issue as the most important issue and will continue to make utmost efforts to realize the return home of all abductees at the earliest possible date while working closely with relevant countries, including the U.S.
【5 Addressing the Situation in the Middle East】
Japan imports approximately 90% of its crude oil from the Middle East, and it is extremely important for Japan's peace and prosperity to promote peace and stability in the Middle East and to maintain and develop good relations with countries in the region. From this point of view, Japan recently has been striving to strengthen its relations with Middle Eastern countries in a wide range of fields that include not only the economy but also politics and security as well as cultural and people-to-people exchanges. Tensions in the Middle East remain high in recent years. In response to the situation, Japan will continue to make active efforts to ease tensions and stabilize the situation in the region. To ensure the safety of Japan-related vessels, Japan has been conducting information gathering activities by Self-Defense Force vessels and aircraft in Middle Eastern waters since 2020 and will make ongoing efforts to ensure the safety of Japan-related vessels in the region.
【6 Leading International Efforts to Create New Rules】
The world economy faces challenges, such as the rise of protectionism and trade disputes, as well as the stagnation of economic activities, plummeting demand, and restrictions on movement of people due to COVID-19. Under such circumstances, Japan has continued its trade liberalization and rule-making efforts through economic partnerships, signing the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) Agreement in November 2020 and the entry into force of the Japan-UK Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (Japan-UK CEPA) in January 2021. In order to expand the free and fair economic order that will serve as the basis for Japan's peace and prosperity in Japan, Japan will continue to make proactive efforts to ensure the early entry into force and full implementation of the RCEP Agreement, steady implementation and expansion of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP11 Agreement) as the chair of the TPP Commission in 2021, and negotiation of other economic partnership agreements.
In addition, in the field of digital technology that will gain importance in the post-COVID-19 world, Japan will globally promote the “Osaka Track,” launched on the margin of the G20 Osaka Summit under Japan's presidency, and lead the efforts to develop common rules on data flow. Japan has focused on building international rules in new areas including new domains such as cyberspace and outer space as well as maintaining national security in our economy and technology which has broadened its scope due to technological innovations, through activities at the UN and other fora. This effort is based on the understanding that existing international law applies to these new areas. Furthermore, Japan will continue to exercise international leadership in disseminating and implementing the principles and visions put forward by Japan at the G20 Osaka Summit, including the “G20 Principles for Quality Infrastructure Investment” and the “Osaka Blue Ocean Vision.”
【7 Addressing Global Challenges】
One country alone cannot address global challenges, such as peacebuilding, terrorism, disarmament and non-proliferation, the rule of law, human rights, women's empowerment and gender equality, disaster risk reduction, global health, and the environment and climate change, and the international community needs to mount a united response. Japan will continue to advance international contributions under the concept of human security in order to ensure that freedom, democracy, human rights and the rule of law are respected as universal values in the international community, to take good care of socially vulnerable people, and to realize a society where individuals can make the most use of their potential. Japan will also accelerate concrete initiatives domestically and internationally in order to lead the global effort for achieving the SDGs.
(Global Health)
Health is critically essential for the embodiment of human security, which is a concept of protecting individuals and unleashing their potential. In order to promote Universal Health Coverage (UHC) with the spirit of “leaving no one's health behind,” Japan has made significant achievements in infectious disease control, maternal and child health and nutrition, in cooperation with other countries and international organizations. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, Japan has offered health and medical services to developing countries for coping with COVID-19, as well as necessary support for building quality, resilient and inclusive medical and health systems from a mid- to long-term perspective, including support for establishing the ASEAN Centre for Public Health Emergencies and Emerging Diseases. In 2021, Japan will host the Tokyo Nutrition for Growth Summit 2021 and promote global efforts toward nutrition improvement.
(Climate Change)
Addressing climate change is increasing in importance, also in the context of the recovery from the COVID-19 crisis. At the 24th Session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP24) in 2018, the implementation guidelines of the Paris Agreement were adopted. Regarding negotiations on the implementation guidelines for market mechanisms, however, an agreement was not reached even at COP25 in 2019, and the guidelines are still under review. Japan will continue to lead the international community in the lead-up to COP26 in 2021 in order to realize a decarbonized world, which the Paris Agreement aims for.
(Proactive Initiatives for Disarmament and Non-Proliferation)
As the only country to have ever suffered atomic bombings in war, Japan has the responsibility to lead the international efforts to realize a world free of nuclear weapons. Japan continues to pursue bridge building between nuclear-weapon states and non-nuclear-weapon states through such actions and frameworks as submission of the resolution on nuclear disarmament to the UN General Assembly, the Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Initiative (NPDI) and the Group of Eminent Persons for Substantive Advancement of Nuclear Disarmament, and has carried out realistic and practical measures that also involve nuclear-weapon states.
In addition, Japan puts effort into non-proliferation policies, including through maintaining and strengthening international non-proliferation regimes and rules, appropriately implementing non-proliferation measures in Japan, as well as closely coordinating with other countries and providing capacity building assistance. Japan places importance on maintaining and strengthening the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), which is the cornerstone of the international nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation regime, and will make active contributions to international discussions to achieve a meaningful outcome at the NPT Review Conference expected to be held in August 2021.
(Strengthening Cooperation with the UN and International Organizations / UN Security Council Reform)
Japan has played a key role in maintaining international peace and security, making contributions through UN Peace Keeping Operations (PKOs) and serving as a non-permanent member of the UNSC 11 times, the most among the UN Member States. Now, with 75 years having passed since the UN was established, it is an urgent issue to make the body more efficient and effective, and suitable for the 21st century. Japan will continue to make efforts in pursuit of the early realization of UNSC reform and Japan's admission as a permanent member. Furthermore, in order to continue to contribute to the order of peace and security in the international community prior to its admission as a permanent member, Japan is seeking to be elected in the UNSC non-permanent membership election in 2022.
In addition, Japan has been making policy contributions, assessed and voluntary financial contributions, as well as personnel contributions in a broad sense for the UN and other international organizations to tackle a variety of issues. Japan will make efforts to encourage the employment of more Japanese staff and their appointment to executive posts at international organizations.
(Africa)
While Africa has made remarkable growth in recent years, it has also faced many challenges. Japan has been contributing to African development through the Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD), the pioneering forum of its kind, launched by Japan in 1993. Japan's initiatives through the TICAD process that support African health and medical systems in the mid- to long-term have shown concrete results in the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. As COVID-19 sheds light on Africa's development issues, including those in the health sector, and looking ahead to TICAD8 to be held in Tunisia in 2022, Japan will continue to strengthen its relations with Africa and to resolutely support African-led development through initiatives that leverage Japan's advantages and its unique characteristics.
 The four foreign ministers attending the Second Japan-Australia-India-U.S. Foreign Ministers' Meeting (October 6, Tokyo)
The four foreign ministers attending the Second Japan-Australia-India-U.S. Foreign Ministers' Meeting (October 6, Tokyo)The four countries of Japan, Australia, India and the U.S. share basic values. Moreover, as responsible partners of the region, they share the common goal of reinforcing a free and open international order based on rules. The “Free and Open Indo-Pacific” vision plays an important role toward the achievement of this goal. To that end, the four countries have been engaging in a wide range of discussions aimed at advancing concrete cooperation on common issues, including quality infrastructure, maritime security and counter-terrorism.
Against this backdrop, Minister for Foreign Affairs of Australia Marise Payne, External Affairs Minister of India Subrahmanyam Jaishankar and Secretary of State of the U.S. Mike Pompeo convened on October 6 in the Iikura Guest House in Tokyo, where Mr. Motegi, Minister for Foreign Affairs chaired the Japan-Australia-India-U.S. Foreign Ministers' Meeting and dinner. This is the second meeting of the four foreign ministers after the inaugural meeting held in New York in September 2019, on the sidelines of the United Nations General Assembly. This was the first meeting held independently and separately from an international conference or other event. Furthermore, as this was also the first international ministerial-level conference to take place in Japan since the outbreak and spread of the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), it was held with the necessary measures in place to prevent the spread of infections.
At the meeting, the four Ministers exchanged views on the response to various challenges that have come to the fore with the outbreak and spread of COVID-19, and affirmed their intention to continue their cooperation in the areas of health and hygiene and on issues including making new international rules in such areas as digital economy. They affirmed the importance of broadening cooperation with more countries for the realization of a “Free and Open Indo-Pacific,” as the vision serves for the peace and prosperity of the region and its importance in the post-COVID-19 world is increasing. They also exchanged views on regional affairs such as North Korea and the East and South China Seas. They then shared the view to regularize this Foreign Ministers' meeting and hold the next one at an appropriate timing next year.
With the global spread of COVID-19, the existing international order is facing challenges in various fields. In light of that, it was timely for the foreign ministers of four countries that share a common purpose to take time and exchange honest views about their recognition of the current situation and response measures for the future.
Japan, Australia, India and the U.S. will continue to steadily advance various forms of cooperation as close partners, in order to achieve a free and open Indo-Pacific and secure the stability and prosperity of the region.
 The foreign ministers of Australia, India and the U.S paying a courtesy call to Prime Minister Suga before the meeting (October 6, Tokyo; Photo: Cabinet Public Relations Office)
The foreign ministers of Australia, India and the U.S paying a courtesy call to Prime Minister Suga before the meeting (October 6, Tokyo; Photo: Cabinet Public Relations Office)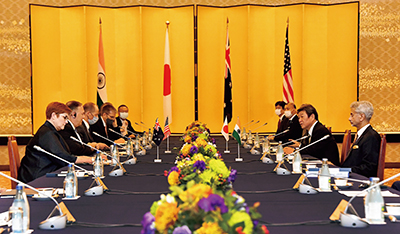 At the Japan-Australia-India-U.S. Foreign Ministers' Meeting (October 6, Tokyo)
At the Japan-Australia-India-U.S. Foreign Ministers' Meeting (October 6, Tokyo)
