Japan's Official Development Assistance White Paper 2005
Chapter 1 Japan's ODA Budget
Section 1. Fiscal Year 2005 ODA Budget (Original Budget)
Major Points in the Fiscal Year 2005 ODA Budget
Secure the expenses necessary for implementing strategic and effective assistance and promote focused assistance in line with the ODA Charter

Focused Assistance in Line with the ODA Charter
1. Promotion of "human security"
—Secure grant aid for "human security"
Grant aid for grassroots human security projects ¥15 billion → ¥14 billion)
Grant aid for infectious diseases prevention and treatment ¥11 billion → ¥11.5 billion)
Grant aid for water security and global environment ¥23 billion → ¥23.5 billion), etc.
—Increase amount of technical cooperation provided by JICA (AIDS and hunger countermeasures, strengthening the administration function in countries with weak governance) (+¥600 million)
2. Assistance for building and consolidation of peace
—Maintain level of emergency grant aid, which was significantly increased in FY2004
(portion that is grant aid for reconstruction and development: ¥26.7 billion - ¥26.8 billion)
—Increase amount of technical cooperation provided by JICA for reconstruction assistance to Iraq and Afghanistan, etc. (+¥200 million)
3. Promotion of aid visibility
—Secure technical cooperation budget (JICA operating cost subsidy:
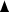 0.7%)
0.7%)—Increase grant assistance for Japanese NGO projects ¥2.7 billion → ¥2.85 billion)
—Promote acceptance of foreign students into Japan
Government-financed students (new) 5,243 → 5,263 (increase of 20)
Corporate assistance to reduce/exempt tuition fees for privately-financed students
15,405 → 15,617 (increase of 212), etc.
Implementation of Strategic and Effective Assistance
1. Establish a system to implement strategic and effective assistance
—Substantially increase the number of grant aid for grassroots project surveyors
(¥280 million → ¥1.0 billion, 71 people → 270 people)
—Strengthen local ODA task forces ¥29 million → ¥48 million)
—Enhance evaluation
(external audit-related honoraria: ¥14 million → ¥15 million, evaluation-related training: ¥0 → ¥40 million)
2. Reduce expenses by streamlining and improving efficiency of projects
—Costs saved by using discounted fares
(e.g., publicly recruited ODA project monitors (¥45 million → ¥37 million, 72 people → 108 people) )
—Expenses saved in technical cooperation provided by JICA
(e.g., reviewing unit costs of equipment provision) (
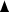 ¥2 billion)
¥2 billion)Chart 1. Changes in the ODA Budget

Chart 2. ODA Budget

Chart 3. General Account Budget

Chart 4. Breakdown of the ODA Project Budget

Chart 5. ODA General Account Budget (for the Entire Government)

Chart 6. ODA Project Budget (for the Entire Government)

Chart 7. Financial Resources for the ODA Project Budget and Expenditure by Type of Assistance

Section 2. Project Budget for ODA-related Ministries and Agencies (Original Budget) and Project Outlines
Chart 8. ODA Budget Changes for Ministries and Agencies (General Account Budget)

Chart 9. ODA Budget Changes for Ministries and Agencies (Project budget)


 Next Page
Next Page