4. Peacebuilding
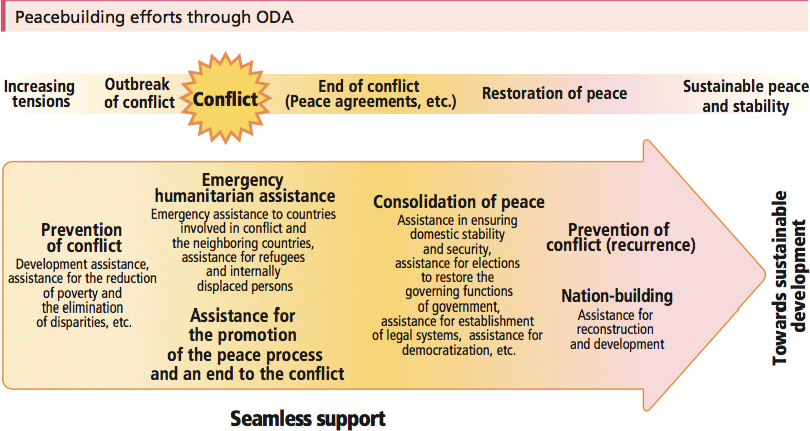
Regional and internal conflicts arising from ethnic, religious, and historical differences continue to pose challenges for the international community. Such conflicts generate a great number of refugees and internally displaced persons (IDPs), leading to humanitarian crises and violations of human rights. Furthermore, these conflicts undermine the progress made through long-term effort, and cause massive economic losses. Therefore, it is important for the entire international community to engage in “peacebuilding” in order to build a foundation for development to prevent conflicts, avoid their recurrence and consolidate sustainable peace. For instance, the UN Peacebuilding Commission, established in 2005, has been engaged in discussions on a consistent approach to support conflict resolution, recovery, and nation-building. The importance of peacebuilding has also been recognized at high levels, on such occasions as the meetings of the United Nations General Assembly.
< Japan's Efforts >

Disabled people receiving welding training through the skills training and job obtainment support for social participation of ex-combatants and other people with disabilities in Rwanda. (Photo: Shinichi Kuno / JICA)
Japan provides various types of supports, including assistance for refugees affected by conflicts, food assistance, and electoral assistance for the peace (political) process. After a conflict is resolved, Japan assists in the Disarmament, Demobilization, and Reintegration (DDR) of former soldiers in order to promote the consolidation of peace. Japan also provides support to rebuild the security sector to ensure domestic security and stability. Japan extends its support to the reconstruction of affected countries by working on the repatriation and resettlement of refugees and IDPs, and rebuilding basic infrastructure. Furthermore, in order to consolidate sustainable peace and prevent the recurrence of conflicts, Japan has been engaged in efforts in social sectors such as healthcare and education as well as reinforcement of the governmental, judicial and police functions, and the development of economic infrastructure and institutions. In such undertakings maximum consideration is given to the importance of the roles that women can play in peacebuilding. In order to provide this support in a seamless manner, Japan also extends bilateral assistance through international organizations together with grant aid, technical cooperation, and ODA loans.
| Human Resources Development for Peacebuilding

Participants from the Primary Course of the “Program for Human Resources Development for Peacebuilding” in FY2013 conducting a group discussion.
Requirements in the field of peacebuilding are becoming more diverse and more complex. In response to these needs on the ground, Japan has conducted the Program for Human Resources Development for Peacebuilding since FY2007 to develop civilian experts from Japan and other regions who will be capable of playing an active role in this field. Pillars of the program consist of coursework in Japan, where participants acquire the practical knowledge and skills required for the peacebuilding field, the Overseas Assignment, where participants work at local offices of international organizations in the peacebuilding field, and support for graduates to build up their careers. To date, 256 nationals from Japan and other countries have participated in the training courses. Many participants who completed the program are now actively working in the field of peacebuilding in countries such as South Sudan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Afghanistan.