Japan's Official Development Assistance White Paper 2009
4. Peacebuilding
Since the end of the Cold War, the international community has confronted numerous regional and internal/intrastate conflicts arising from ethnic, religious, or historical differences. Such conflicts generate a great number of refugees and internally displaced persons and easily become humanitarian and human rights issues. Moreover, such conflicts destroy many achievements gained through years of development efforts and cause massive economic loss. In light of this, the UN General Assembly and the Security Council jointly adopted a resolution to establish the Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) in 2005. The PBC makes advice and proposals based on a consistent approach, beginning with resolution of conflicts and continuing to recovery, reconstruction, and nation-building.
<Japan's Efforts>
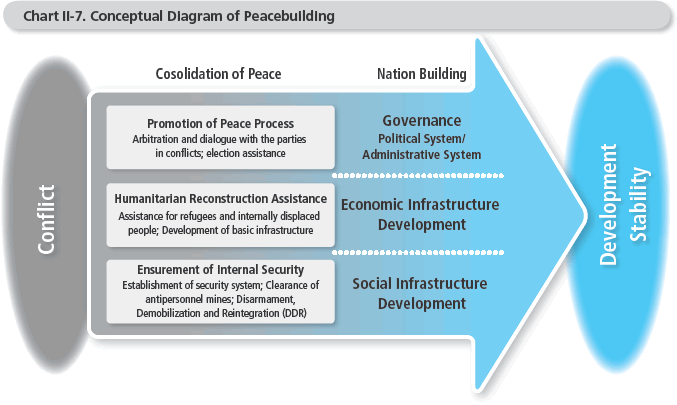
As for specific efforts, Japan has provided assistance, including refugee assistance and food aid in times of conflict, and assistance in the area of the peace process, such as election assistance. Assistance is provided in the aftermath of conflicts, to ensure domestic security and safety, with the aim of consolidating peace, including assistance to the disarmament, demobilization, and reintegration (DDR) of former soldiers and reconstruction efforts in the security sector. Additionally, Japan has supported reconstruction by promoting efforts for the return of refugees and internally displaced persons and their resettlement, as well as by restoring basic infrastructure.
Furthermore, in order to establish consolidated peace and prevent the rise of another conflict, efforts are made in the social sector such as in health and education, as well as toward improving economic infrastructure, and strengthening governmental, judicial, and police functions. Japan combines assistance provided via multilateral organizations with bilateral assistance, such as grant aid, technical cooperation, and loan aid, in order to provide this type of seamless assistance.
In June 2007, Japan was selected as the chair of the United Nations Peacebuilding Commission due to its efforts in the area of peacebuilding to date. During its term as the chair until December 2008, Japan made efforts to strengthen and consolidate the activities of the Commission, including strengthening collaboration with the United Nations Security Council, enhancing relations with the World Bank, IMF, and regional organizations, and spurring interest in and calling for support for target countries.
• Human Resource Development for Peacebuilding
In light of the needs from the scene of peacebuilding becoming more diverse and complex, Japan launched the Program for Human Resource Development in Asia for Peacebuilding in FY2007 to foster experts needed at the site of peacebuilding. In FY2008, like the previous year, the initiative had approximately 30 program associates from Japan and other Asian countries and offered three pillars as follows: (1) Coursework in Japan; (2) Overseas attachment; and (3) Career development support. Many program associates who completed the programs are now actually working in the field of peacebuilding, in locations such as Sudan and Timor-Leste. A Senior Specialist Course was conducted in FY 2009 to enhance the program from the perspective of using the vitality of seniors in both the public and private sectors in peacebuilding. Senior experts with specialized knowledge that can be of use in places where peacebuilding is taking place are given the necessary training and are dispatched to actual fields.
(1) Iraq
The international community has been extending assistance for Iraqi nation building to restore and establish peace and stability in Iraq. It is extremely important for the peace and stability of the international community including the people of Iraq, the Middle East and Japan to rebuild Iraq as a peaceful democratic country. A new government was inaugurated in 2006 as a result of the Iraqi National Assembly election held in 2005. In May 2007, a ministerial-level meeting was held in Egypt to conclude the International Compact with Iraq—a compact that stipulates the cooperative roles of the Iraqi government and international society in a wide range of sectors, including politics, security, economy, and society—74 nations and organizations affected. It is expected that the international community will lend assistance so as to allow the Iraqi government to have more self-reliant and autonomous efforts.
<Japan's Efforts>
To date, Japan has conducted the reconstruction assistance of Iraq by combining the humanitarian activities of Self-Defense Forces (SDF) and official development assistance as an "inseparable pair." Regarding assistance by the SDF, the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force engaged in humanitarian reconstruction activities including the rehabilitation and development of public medical, water provision, and school facilities centered in Samawah from the beginning of 2004 until July 2006. Transport support for personnel and goods of the UN and the multinational forces by the Japan Air Self-Defense Force ended in December 2008.
As for official development assistance, Japan's direct assistance through grant aid has reached approximately US$1.7 billion in total as of the end of FY2008. Japan has also been assisting capacity building of Iraqi administrative officials and engineers through training programs in various areas. As of the end of FY2008, approximately 3,100 Iraqis have received training in Japan and in Iraq's neighboring countries such as Egypt and Jordan. Regarding loan aid, after discussion with the Iraqi side and conducting various studies, Japan decided the provision of approximately US$2,430 million of funds necessary to implement 12 projects in the sectors of power, transportation, petroleum, irrigation, and others, by the end of FY2008.
Furthermore, in order to address Iraq's debt problems, an agreement was reached in 2004 at the Paris Club that 80% of Iraq's total Paris Club debt of US$37.2 billion be reduced over three stages. Based on this agreement, an Exchange of Notes took place in November 2005 between Japan and Iraq, which would reduce Iraq's total debt owed to Japan of approximately US$7.6 billion (Japan is the number one creditor nation to Iraq) by 80% in total over the three stages. Then, the debt reduction was completed for a total of approximately US$6.7 billion with the final reduction in December 2008.
In the Province of Al-Muthanna, the central city of which is Samawah, the Government of Japan has provided assistance of more than US$200 million in total through development assistance in the forms of Grant Assistance for Grass-Roots Human Security Projects and Emergency Grant Aid in coordination with the activities of the SDF. In particular, the Government has placed priority on the following issues: provision of safe drinking water, stabilization of the electricity supply, provision of basic medical services, improvement of sanitary conditions, improvement of the educational environment, maintenance of community roads, creation of employment opportunities, restoration of public safety for people's lives, and development of human resources.
