The Hague Convention (Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction)
For Those Who File a Petition for Conciliation (Adjudication) for Visitation or Contacts under the Hague Convention Implementation Act
1 Cases Where Conciliation (or Adjudication) Procedures [Note] for Visitation or Contacts are Handled by Tokyo or Osaka Family Court under the Hague Convention Implementation Act
According to the law of Japan, a parent who has not taken care of his/her child, during separation or after the divorce, may file a petition for conciliation (or adjudication) to seek visitation or contacts with the child, and may file a petition for conciliation (or adjudication) to seek modification of the contents or of the method, etc. of the visitation or contacts already set up, if circumstances (substantial aspects such as the age or other situations) have been changed. In such a case, in principle, conciliation is to be filed to the family court with the jurisdiction covering the address of the respondent, and adjudication is to be filed to the family court with the jurisdiction covering the address of the child. Under the Act for Implementation of the Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction (the Hague Convention Implementation Act) , however, if a decision has been made by the Minister for Foreign Affairs either for providing assistance in child's return to foreign state or assistance in visitation or contacts with child in Japan, or a petition for the return of child has been filed, you may take procedures for conciliation (or adjudication) for visitation or contacts also at Tokyo Family Court or Osaka Family Court.
If the court where petitioner files a petition does not have the jurisdiction, such case may be transferred to another court. Further, even if Tokyo Family Court or Osaka Family Court has jurisdiction under the Hague Convention Implementation Act, the case may be transferred to the court nearest to the address of the child or of the respondent considering various circumstances including necessity of a prompt investigation of the child's situation.
[Note] Conciliation and its procedures are explained in detail in the next section. "Adjudication" is a judge's final decision in domestic relation cases and "adjudication procedures" is a generic term for the procedures relating to adjudication.
【Cases where conciliation (or adjudication) for visitation or contacts with child is also handled by TOKYO FAMILY COURT】
- (1) In the case where the address of the child (if the child's address is not in Japan or not known, the child's residence applies) is located in the following places
- Within Jurisdiction of Sapporo High Court ------ Hokkaido
- Within Jurisdiction of Sendai High Court -------- Miyagi, Aomori, Akita, Iwate, Yamagata, Fukushima
- Within Jurisdiction of Tokyo High Court -------- Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba, Saitama, Gunma, Ibaraki, Tochigi, Yamanashi, Niigata, Nagano, Shizuoka
- Within Jurisdiction of Nagoya High Court ------- Aichi, Gifu, Mie, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui
- (2) In the case where the address of the child is not in Japan or not known, and the residence of the child is not in Japan or not known.
【Cases where conciliation (or adjudication) for visitation or contacts with child is also handled by OSAKA FAMILY COURT】
- In the case where the address of the child (if the child's address is not in Japan or not known, the child's residence applies) is located in the following places
- Within Jurisdiction of Osaka High Court -------- Osaka, Kyoto, Hyogo, Nara, Shiga, Wakayama
- Within Jurisdiction of Hiroshima High Court ----- Hiroshima, Okayama, Yamaguchi, Tottori, Shimane
- Within Jurisdiction of Fukuoka High Court ------ Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Oita, Kumamoto, Kagoshima, Miyazaki, Okinawa
- Within Jurisdiction of Takamatsu High Court ---- Kagawa, Tokushima, Kochi, Ehime
Although it is not mandatory to appoint an attorney in the procedures for conciliation (or adjudication) for visitation or contacts, you may need legal knowledge of both Japan and the state of habitual residence of the child, etc. in order to examine which state's law to apply in the arrangement of visitation or contacts, in what cases the petitioner can have visitation or contacts with the child under the law to be applied, and if the arrangement on visitation or contacts has effect also in the state of habitual residence. Furthermore, all written documents to be submitted to the court should be prepared in Japanese. For these reasons, the person who is considering to file a petition to the court is advised to consult with an attorney of Japan. Once you appoint an attorney, the attorney will carry out, as your agent, alleging and proving including preparation of necessary documents.
If you are interested in introduction to Japanese attorneys, please refer to Lawyer Referral Service for Hague Convention Cases or contact the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which is the Central Authority of Japan.
or contact the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which is the Central Authority of Japan.
Hague Convention Division, Consular Affairs Bureau, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Address:Kasumigaseki 2-2-1, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, Japan, 100-8919
Telephone Number:+81-3-5501-8466
Email Address:hagueconventionjapan@mofa.go.jp
2 Conciliation Procedures are Shown as Follows
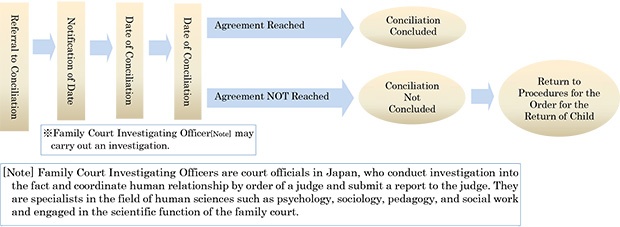
Conciliation Procedures are presided by a Conciliation Committee and aim for reconciling the opinions and formulating agreement between both parties. The Conciliation Committee first makes inquiry on circumstances and hears opinions from both parties. Then the Conciliation Committee provides advice or recommendation from a neutral and fair standpoint. The Conciliation Committee usually consists of one judge and two or more committee members who are selected citizens with commonsense from non-governmental sector. In conciliation procedures, both parties are required to appear in principle.
The flow of conciliation procedures are shown in the diagram below. On the designated date, the petitioner and the respondent, after waiting in the respective waiting rooms are to enter a conciliation room alternately or at the same time. The Conciliation Committee facilitates discussion from a neutral position while hearing from both parties. The conciliation Procedures are closed-door procedures.
It is desirable that an arrangement about visitation or contacts with the child is made by an agreement of both parties through discussion between them. Even when a court is examining a petition for the return of child to the state of habitual residence in parallel, agreement through discussions between both parties as to whether the child should be returned to the state of habitual residence is desirable. For example, in a case where you assume that the child should be returned to the state of habitual residence, you may need to arrange visitation or contacts for the time being in the state of habitual residence. In a case where you assume that the child should continue to live in Japan as accustomed so far, you would need to arrange visitation or contacts in this case, too. For this reason, even if at first a petition for adjudication for visitation or contacts was filed, it may be referred to conciliation procedures by a decision of the judge.
3 How to Submit Documents, etc. Required for Procedures
- In the conciliation, both parties may be requested to submit documents to support your argument depending on the necessity. As for the ways to submit the documents, ask the Conciliation Committee member in charge or a court clerk.
- Be sure to attach a Japanese translation to an evidentiary document written in a foreign language.
4 Inspection of or Copying of the Submitted Documents
A copy of the written petition submitted by the petitioner is sent to the respondent as specified by the law. Besides that, one party may request for inspection of or copying of the documents, etc. submitted by the other party during conciliation procedures. The judge will make a decision whether to permit the request considering circumstances including if the request is obstructing a smooth discussion. In the case where adjudication procedures commences with a non-conclusion of conciliation, the judge of adjudication procedures examine the documents submitted during the conciliation procedures if the documents are necessary for adjudication. Then a request for inspection of or copying of the documents is permitted as long as the legally specified grounds for exception do not apply. This is the same manner to the case where a petition is filed for adjudication from the beginning.
5 What to Confirm before Filing a Petition
(1) Assistance from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (the Minister for Foreign Affairs)
In the case you file a petition for conciliation (or adjudication) for visitation or contacts to Tokyo Family Court or to Osaka Family Court according to the Hague Convention Implementation Act, the precondition is that you have received the decision of the Minister for Foreign Affairs either for assistance in child's return to foreign state or for assistance in visitation or contacts with child in Japan, or you have filed a petition for the return of child.
In addition, if the address of the child, and the name and address of the person who lives together with the child are not identified, the court will not be able to take any further procedures. However, when the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (the Minister for Foreign Affairs) decides to provide assistance in visitation or contacts, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (the Minister for Foreign Affairs) will collect information from related organizations to discover the whereabouts of the child and to identify the name and address of the person who live together with the child. Therefore, for prompt proceedings, you are advised to file an application for assistance to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (the Minister for Foreign Affairs) before filing a petition to a court.
(2) Prepare a place within Japan to receive documents from the court
You are requested to designate a place to receive documents from the court, when you file a petition. Basically the court will send documents including a written order, etc. to the place you specified. If the address specified is in a foreign state, the court cannot take smooth procedures as it would need much more time for the process to send the documents. Therefore, the receiver's address should be in Japan. If you appoint a Japanese attorney, you may specify the office address of your attorney as the receiver's address.
(3) Investigations on Laws of the State of Habitual Residence
The effectiveness of an agreement on visitation or contacts in the state of habitual residence may depend on interpretation of laws of the state. For this reason, both parties in the conciliation procedures may be requested to investigate laws of the state of habitual residence.

