Diplomatic Bluebook 2023
Chapter 4
Japan's Diplomacy Open to the Public
2 Strengthening the Foreign Policy Implementation Structure
As we fully enter an era of competition among nations, Russia launched aggressions against Ukraine and shook the very foundation of the international order. In the Indo-Pacific region as well, there are countries unilaterally changing, or attempting to change, the status quo by force, and Japan is facing the most severe and complex postwar security environment. To promote diplomatic power for maintaining and developing an international order based on universal values, it is vital to fundamentally strengthen the foreign policy implementation structure. To that end, MOFA is working on strengthening its diplomatic missions overseas in both the aspects of quantity and quality, as well as advancing efforts to improve the organizational and personnel systems at MOFA itself.
Diplomatic missions overseas, such as embassies and consulates-general, not only represent Japan and engage in diplomatic activities, but also play a key role in areas such as information-gathering and strategic communication at the frontline of diplomacy. At the same time, overseas missions also carry out operations directly related to enhancing the interests of Japanese nationals, such as protecting their lives and safety, providing support for Japanese companies, promoting investment and tourism, and securing energy and other resources.
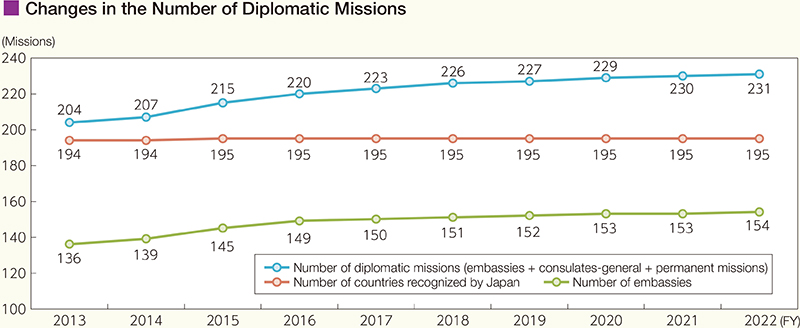
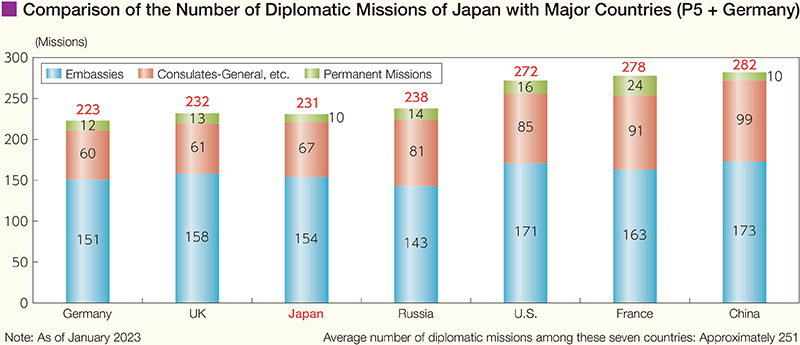
In January 2023, Japan established the Embassy of Japan in Kiribati. As a result, the number of diplomatic missions overseas as of fiscal year (FY) 2022 is 231 (154 embassies, 67 consulates-general and 10 permanent missions).
Kiribati is a key junction in the South Pacific with an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) that is the largest among Pacific Island countries and the 12th largest in the world. Deepening Japan-Kiribati cooperative relations is essential for the realization of a “Free and Open Indo-Pacific” (FOIP). Furthermore, Kiribati is an important partner that has often supported Japan's position at international fora. It is vital that Japan establish an embassy there to continue maintaining and strengthening the favorable bilateral relationship and enhancing the system for more effective gathering of various information and provision of assistance in emergency situations.
In FY2023, Japan will establish an embassy in Seychelles as well as a Permanent Mission of Japan to the International Organizations in Rome, Italy (independent office). There are also plans to establish an independent office for the Mission of Japan to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
Seychelles is located along sea lanes that are important to the security and economy of the Indo-Pacific region, making it an important country for the realization of FOIP. Furthermore, it is positioned along a maritime route that connects Mombasa Port in Kenya, East Africa's largest commercial port, which Japan is helping to develop, the Nacala Corridor in Mozambique, and Toamasina Port in Madagascar. With its rich fishery resources, Japanese companies are also showing interest in expanding their businesses to Seychelles. Seychelles also supports Japan in areas such as important international elections. Hence, establishing an embassy in Seychelles is important not only for maintaining and strengthening the friendly bilateral relations between the two countries so far, but also for strengthening systems to enhance effectiveness in collecting information and providing various forms of support in emergencies.
Rome is the base of international organizations working in the areas of food and agriculture, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations World Food Programme (WFP), and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD). These three international organizations work in close cooperation with one another to secure global food security and reduce the number of hungry people, through initiatives to stabilize the global food markets and particularly by providing food support to countries vulnerable to factors that destabilize the food market and improving the production and distribution of agricultural produce. Amidst rising food prices due to the impact of disruptions in the food supply chain as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, destabilization of grain supply due to Russia's aggression against Ukraine, and other factors, it is vital for Japan, in advancing its diplomacy, to secure Japan's food security and help to stabilize the global food market, including facilitating access to food by countries that are particularly vulnerable to the impact of such factors. It is becoming increasingly important to cooperate with the three organizations in Rome that work to address food and agriculture issues, and establishing a Permanent Mission of Japan is important in contributing toward strengthening Japan's presence, and to the development of systems for cooperation and forming close networks with the three organizations.
The Mission of Japan to NATO has, till now, been based in the Embassy of Japan in Belgium as it worked to gradually strengthen Japan's relationship with NATO. NATO, too, has been increasing their interest in the Indo-Pacific region, as shown by their accord to expand cooperation with Asia Pacific partners, including Japan, at the NATO Summit Meeting held in June 2021. Against this backdrop, Russia's aggression against Ukraine, launched in February 2022, clearly showed that the security of Europe and of the Indo-Pacific regions are inseparable, a point that Japan emphasized through the attendance of Foreign Minister Hayashi and Prime Minister Kishida at a NATO Foreign Ministers' Meeting in April and a NATO Summit in June. Against the backdrop of challenges to the international order based on the rule of law, it is extremely important to strengthen cooperation among like-minded countries that share fundamental values. In view of this growing need to further strengthen cooperation between Japan and NATO, and with the expectation of greater opportunities for Japan-NATO cooperation that will also contribute to the realization of FOIP, such as through the implementation of concrete cooperation across wide-ranging areas of partnership, it is important to establish the Mission of Japan to NATO.
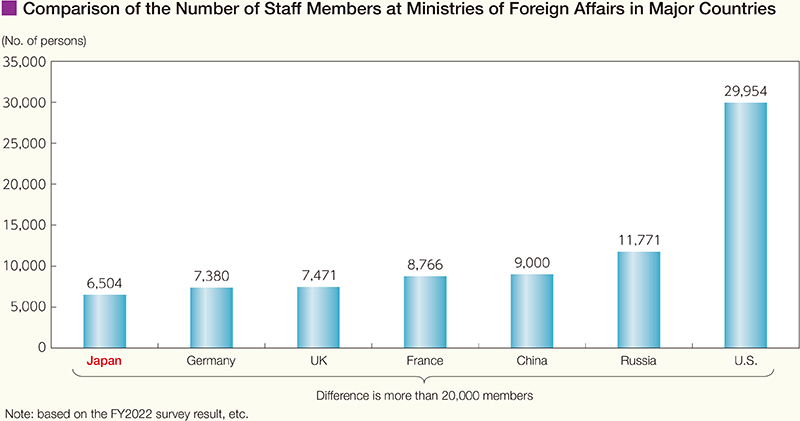
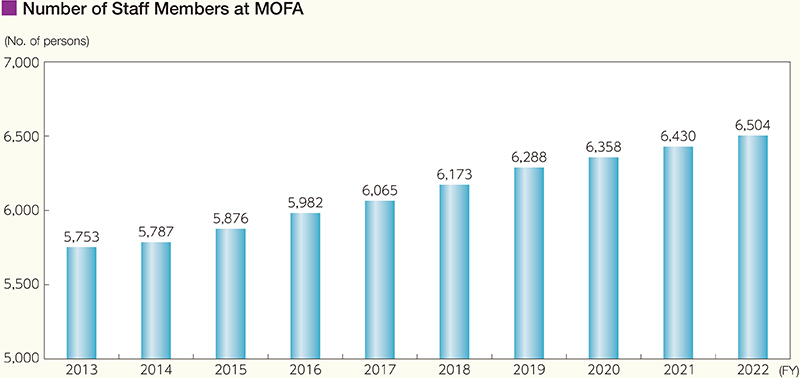
In addition to establishing more diplomatic missions overseas, it is important to secure and increase the number of staff members to support diplomacy at the MOFA headquarters and diplomatic missions overseas. In the context of the Government's policy to reduce the overall personnel expenses due to the current severe budget situation, the number of staff members at MOFA was increased to 6,504 in FY2022 (6,430 in FY2021) in order to address bilateral relations and regional situations, secure peace and stability and conduct strategic communications, promote economic diplomacy, contribute to addressing global issues, and implement protection and safety measures for Japanese nationals abroad. The number of staff members, however, remains insufficient in comparison with other major countries. MOFA continues its efforts to build a structure that is commensurate with Japan's national power and diplomatic policy. In the meantime, based on the belief that enhancing the foreign policy implementation structure remains essential in FY2023, MOFA will increase its workforce by 100 staff.
In order to protect universal values in the international community and conduct diplomacy with a balanced and stable posture with a high level of responsiveness, MOFA appropriated 707.4 billion yen in the budget for FY2022 (of which 17 billion yen is appropriated in the budget of the Digital Agency). Furthermore, MOFA appropriated 267.3 billion yen in the supplementary budget for FY2022 (of which 2.57 billion yen is appropriated in the Digital Agency budget). The funding appropriated in the budget included funding for Japan to exercise its leadership as the G7 Presidency and a Non-permanent Member of the UN Security Council, to support Ukraine, and for measures to engage in flexible and firm diplomacy, particularly in the realization of FOIP. Furthermore, funding was also appropriated for measures to respond to the severe yen depreciation and high prices.
MOFA's FY2023 initial government budget proposal appropriated 756 billion yen (of which 12.5 billion yen is appropriated in the Digital Agency budget) based on the following priorities: (1) maintaining and developing an international order based on universal values in an era of competition among nations; (2) strengthening response to new forms of warfare, including information warfare; (3) strengthening initiatives to promote human security and address global issues; and (4) fundamentally strengthening the foreign and consular policy implementation structure. This includes budgets for holding the G7 Hiroshima Summit and projects to mark the 50th Year of ASEAN-Japan Friendship and Cooperation, realizing FOIP including support to like-minded countries for capacity building in the field of security, supporting Ukraine and countries affected by the situation in Ukraine, promoting economic security, strengthening capacity to analyze the international situation by using AI, and conducting flexible and proactive diplomacy.
In order to promote Japan's national interests, Japan will continue to proceed strategically to develop the foreign policy implementation structure and enhance it further, while making efforts to streamline operations.