Japan's Official Development Assistance White Paper 2011
7. Oceania
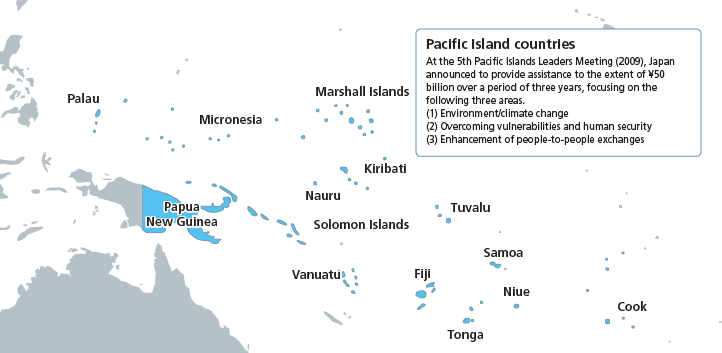
The Pacific Island countries are not only Japan's neighbors that share the Pacific Ocean, but also have historical ties to Japan. Having an enormous Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), these countries and regions are the cornerstone of Japan's maritime transport, and provide important deep-sea fishing grounds. The peace and prosperity of the Pacific Islands are extremely important to Japan.
Meanwhile, many of the Pacific island countries have achieved independence relatively recently, and there is an urgent need for them to establish themselves as socio-economically self-reliant nations. In addition, there are a number of difficulties that island countries and regions face in particular, such as small-scale economies, dependence on primary industries, geographic dispersion, lack of easy access to international markets, vulnerability to natural disasters, and the risk of losing national territory for rising ocean levels. Further, the region faces problems related to democratization such as political turmoil in Fiji.
Based on such circumstances, Japan provides assistance taking into consideration the situation in each country and region, as a good partner to the Pacific Islands.

A physical therapist of Japan Overseas Cooperation Volunteer provides guidance for a walking exercise in Papua New Guinea (Photo: Masaki Haraguchi)
<Japan's Efforts>
To achieve political stability and self-reliant economic development in the Pacific Island countries, it is crucial to overcome socio-economic vulnerabilities and to provide cooperation for the entire region. In addition to promoting cooperation with the Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) (Note 28), a framework for regional cooperation composed of the leaders of the Pacific island countries, Pacific Islands Leaders Meeting (PALM), which is the summit meeting between Japan and Pacific Island countries, has been held once every three years since 1997.
At the 5th Pacific Islands Leaders Meeting (PALMS) held in Tomamu, Hokkaido in May 2009, Japan committed to provide assistance to the extent of ¥50 billion by the next Summit Meeting in Okinawa scheduled for 2012. In the environment/climate change area, one of the three pillars of this assistance, Japan proposed the initiative of the Pacific Environment Community for cooperation between Japan and the Pacific Islands countries. Japan also provides support to overcome vulnerabilities facing Pacific island countries from the perspective of human security. Further, Japan has implemented the "Kizuna" Plan, promoting people-to-people exchange, including youth exchange for more than 1,000 people in the next three years from 2009 between Japan and the Pacific island countries.
The PALM Ministerial Interim Meeting was held for the first time in October 2010 in order to follow up the outcomes of PALM 5 as well as to prepare for PALM 6.
At the 40th Pacific Islands Forum Leaders' Meeting held in Cairns, Australia in August 2009, the Cairns Compact was adopted with the goal of promoting aid coordination for the development of the PIF member countries and regions. Japan also contributes to the promotion of aid coordination including through the Cairns Compact to achieve effective and efficient development in Oceania.
The Pacific island countries share development challenges in the areas of the environment/climate change, education, and health. In order to achieve the sustainable development of these countries, Japan provides cooperation not only for each individual country, but also engages in regional cooperation that considers the benefit to the entire Pacific region.
For example, in the field of environment and climate change, Japan works together with the South Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP), a regional organization located in Samoa, to support the formulation of the Pacific Regional Solid Waste Management Strategy and capacity development. Moreover, the Pacific Island countries are significantly affected by climate change and are vulnerable to natural disasters. To improve their capacity for disaster prevention, Japan provides support for the measures to address environment and climate change through the establishment of systems that enable residents to escape appropriately.
In the area of education, Japan is supporting the University of the South Pacific (USP), which was founded by 11 countries and 1 area of the Pacific region, in constructing facilities for research on information communication technology and providing equipment. Japan has also assisted the university in improving its distance learning network, which provides the opportunity for higher education for a wide range of people in the Pacific island countries and areas.
In the field of health, Japan implements regional assistance. For example, in order to strengthen immunization projects in the Pacific island countries, Japan has extended assistance in cooperation with the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) to contribute to the achievement of plans to expand immunization, through provision of vaccines and maintenance of vaccine cold chains (Note 29), thereby contributing to the improvement of immunization rates against measles and Type-B hepatitis, etc., in the region.

A satellite communication earth station used for the construction of a distance-learning network (USPNet) as part of the "ICT for Human Development and Human Security Project" in Fiji. Distance-learning programs are provided from this location to remote campuses and learning centers in 12 Pacific Island countries. (Photo: Kader Hiroshi Pramanik)
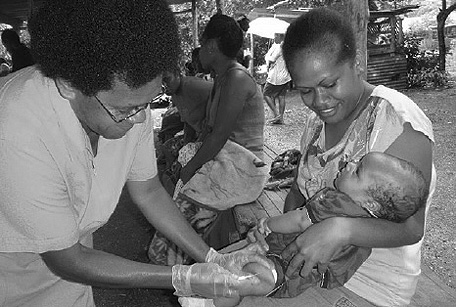
A child is vaccinated in Vanuatu (Photo: Yuki Jimbo)
Notes:
(28) PIF member countries/regions: Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Fiji, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Tonga, Nauru, Kiribati, Tuvalu, Federated States of Micronesia, Marshall Islands, Palau, Cook, Niue
(29) A method of distribution that ensures that vaccines and other pharmaceuticals are kept at a low temperature without interruption throughout the process of production, transport, and consumption.
[Samoa]
"The Project for Enhancing Management Capacity for National Parks and National Reserves of Samoa"
Technical Cooperation Project (March 2007 - September 2010)
Of the countries of Oceania, Samoa is home to a particular diversity and high rate of endemic species of plants and birds. But in recent years, decrease of the area of forests due to deforestation cause big issues such as the decrease in the number of birds. In addition, its geographical characteristics make it easily affected by invasive alien species, which impact biodiversity. Although suitable management of the protected area is necessary to maintain Samoa's valuable natural environment, the management has not been conducted enough due to lack of capable government employees, equipment, and budget. In this respect, Japan provides assistance to formulate plans for the management of major national parks and natural reserves and to improve the awareness of the people around the area. The goal of this project over a period of three years is to enable governmental organizations to formulate management plans on their own and acquire the ability to operate and manage the plans.

Entrance to the Vailima Botanical Garden Reserve
Japan's international cooperation policy in the Oceanian Region