Japan's Official Development Assistance White Paper 2011
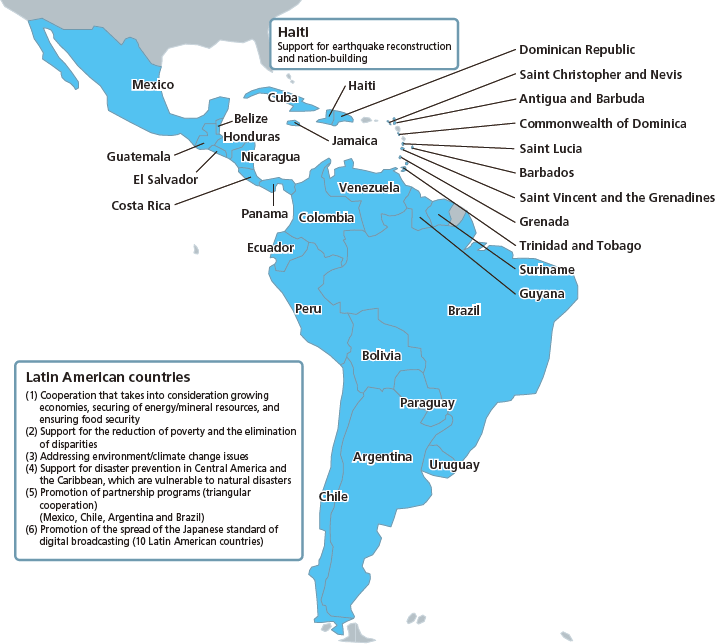
6. Latin America and the Caribbean
With a population of 570 million, Latin America is an enormous market that boasts a regional gross production of $4.8 trillion. The region is also increasing its presence in the international community through the establishment of democracy and continued stable growth, in addition to playing a role as a provider of steel, copper, silver, rare metals, crude oil, natural gas, biofuels, and other minerals and energy resources, as well as food resources. Although the average income level in the region is relatively high among ODA recipient countries, the region is also characterized by a significant income disparity between the rich and the poor, and a large number of people who suffer from poverty. In addition, while the region has an abundance of natural environments such as the Amazon Rainforest, it is also vulnerable to natural disasters like earthquakes and hurricanes, so efforts to address the environment/climate change and disaster prevention are important as well.

Indigenous Ecuadorians till a field at an altitude of 3,500 m in the Andes Mountains
<Japan's Efforts>
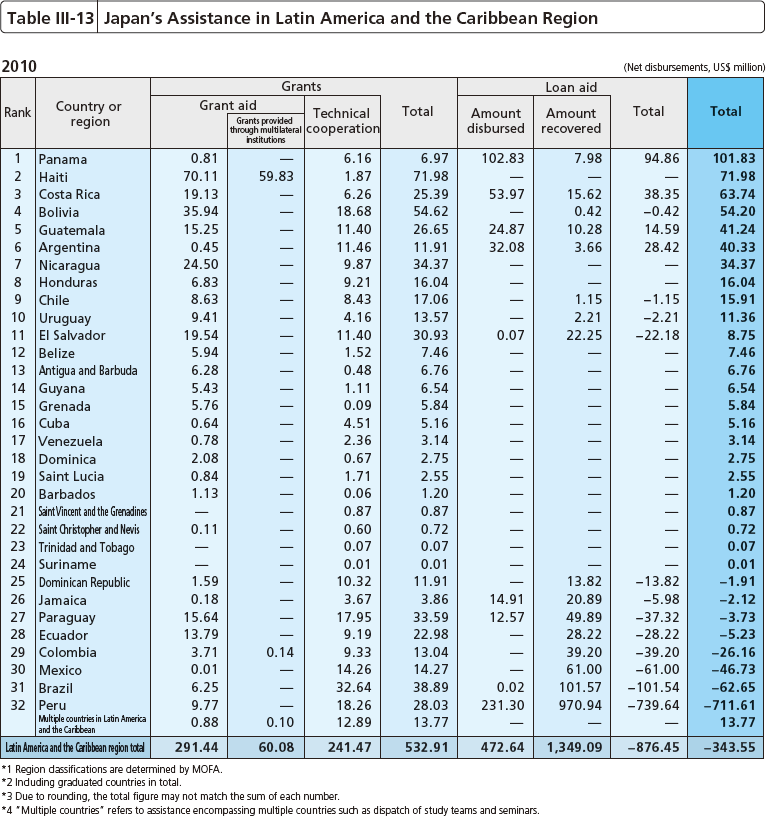
Japan has traditionally had a friendly relationship with the countries of Latin America and the Caribbean. Through ODA, Japan provides support to those countries in achieving sustainable growth, reduction of poverty, correction of disparities, and consolidation of peace, South-South cooperation, etc. Assistance for sustainable growth in Latin America consists of aid for the improvement of infrastructure, the development of small and medium-sized companies, etc. In addition, Japan provides assistance for social development, such as health and medical care, education, and regional development, in order to reduce poverty and improve the income gap, which are historical challenges in the region. Further, Japan has provided an emergency and reconstruction aid to countries affected by natural disasters, such as the earthquake devastated in Haiti in January 2010 and the earthquake occurred in Chile in February 2010.
Japan cooperates with the Central American Integration System (SICA),(Note 26) the Caribbean Community (CARICOM), and other regional communities to formulate wide-ranging projects in order to implement more effective and efficient aid related to development issues that are shared throughout Latin America. The Second Japan-CARICOM Ministerial-level Meeting was held in Tokyo in September 2010. At this meeting, the "Partnership for Peace, Development and Prosperity between Japan and the Member States of CARICOM" was adopted. In addition, Japan announced that it would cooperate with CARICOM in the areas of the integration into the global economy, measures towards environment and climate change, over the next three years or so under the framework of the "Japan-CARICOM Partnership Programme." (see "Terminolozy" on page 25)
Further, many years of Japan's economic cooperation have also allowed it to cooperate with Brazil, Mexico, Chile, and Argentina, which are now entering the stage as influential actors to provide assistance to third countries such as Latin American and African countries under the schemes of Third Country Training Programme and Third Country Expert Dispatch. For example, Japan works together with Brazil to provide agricultural development projects to Mozambique in Africa. Japan also works with Mexico, Argentina, and the Dominican Republic to provide assistance in the reconstruction process after the earthquake in Haiti.
In addition to deforestation and deterioration of the Amazon Rainforest, other environmental problems are deteriorating in Latin America and the Caribbean, such as the growing hole in the ozone layer, declining glaciers in the Andes caused by climate change, and frequent natural disasters such as hurricanes. Japan provides assistance for natural environment conservation and disaster prevention in order to halt these problems and mitigate their impacts.
Under the private-public partnership, Japan cooperates in introducing the Japanese ISDB-T-T(Note 27) standards for terrestrial digital TV. By November 2011, this system has been adopted by ten Latin American countries. Japan supports these countries by transferring technology and training experts to enable smooth implementation of the system.
Moreover, Japan dispatched the Medical Team of Japan Disaster Relief Team and Japanese Self-Defense Force Unit immediately after the earthquake in Haiti, provided medical aid, food, water, and shelters through the cooperation with international organizations and supported relief activities of the Japanese NGOs. At the International Conference towards a New Future for Haiti held in New York in March 2010, Japan pledged as assistance of $100 million, and has been assisting Haiti's national reconstruction, focusing on education, capacity building, health and medical care, and food and agriculture.
Further, after the earthquake in February 2010, Japan provided to Chile, emergency grant aid such as power generators, tents, medical equipment, and the construction of temporary hospitals. In December 2010, when Colombia and Venezuela were suffering from flood caused by continual rain, Japan provided emergency relief goods such as tents and blankets.
Terminology
*South-South Cooperation
Cooperation provided by advanced developing countries to other developing countries, using their own personnel and experiences in development. It is conducted among mainly countries that have similar natural environments and cultural and economic circumstances, and are at a similar stage of development, etc. In addition, support by donors or international organizations for cooperation between such developing countries is referred to as "triangular cooperation." (See page 26)
*Third Country Training
Training provided by developing countries that receive funds and technical assistance from donor countries and international organizations, accept trainees from other developing countries, and transfer/disseminate development experience, knowledge, and technology. Japan provides technical and resource support for such efforts.
*Third Country Specialist
A system for dispatching personnel from developing countries as specialists to other developing countries that are the target of cooperation, for the purpose of providing technical cooperation effectively.
Notes:
(26) SICA: Sistema de la Integración Centroamericana
(27) ISDB-T: Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting- Terrestrial
[Ecuador/Peru]
"Project for Construction of the New Macara International Bridge"
Grant Aid (March 2010 - Current)
Since the border dispute in Peru and Ecuador ended and a peace agreement signed in 1998, the government of Peru and Ecuador formulated a 10-year plan for the purpose of strengthening solidarity and supporting development in border regions of the both countries. As a symbolic project to encourage the consolidation of peace between the two countries, Japan decided to contribute up to ¥1.6 billion in grant aid for the construction of a new 40-ton capacity bridge to replace the current dilapidated Macara Bridge over the border that was a part of the 10-year plan. Japan is working steadily on the construction, aiming for its completion at the end of 2012. The project is expected to promote stable distribution and transport of the workforce, develop the region, mitigate regional disparity, strengthen solidarity in the border region, and encourage the consolidation of peace of the two countries.

A view downstream from the existing Macara Bridge showing pre-construction conditions (as of October 2010). Peru is on the left, and Ecuador is on the right. (Photo: Nippon Koei)

Status of the site as of February 2011 (Photo: Nippon Koei)
[Haiti]
"The Urgent Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Support Project for Haiti"
Technical Cooperation for Development Planning (June 2010 - November 2011)
With its long history of political instability Haiti is the poorest country in Latin America and the Caribbean, and half of the country's people are living on around ¥100 ($1.25) a day or less. In such circumstances the magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck Haiti on January 12, 2010. The earthquake caused enormous damage, resulting in approximately 310,000 deaths and missing persons. Roughly 90% of the buildings in the city of Leogane, near the epicenter, were destroyed. To support Haiti's reconstruction, Japan has provided emergency humanitarian assistance through the Japan Disaster Relief Team. Japan continued to aid Haiti through "the Urgent Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Support Project for Haiti" on the two pillars of "formulation of a reconstruction plan" to delineate a path to reconstruction, and "restoration of social infrastructure" to rebuild the living conditions. As part of this project, a part of the water supply network in Leogane was restored and water lines to eleven schools in the city were established, giving about 9,000 people access to safe water. In addition, it was determined that Japan would support the "Project for Rehabilitation of Urban Roads (Roads and Drainage) in Leogane, Haiti. Japan will provide seamless support for reconstruction of the affected areas.

Children using shared water faucets installed at a school (Photo: Yachiyo Engineering)
Japan's international cooperation policy in the Latin America and the Caribbean Region