Japan's Official Development Assistance White Paper 2007
Box 2. Follow-up on the Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness
1. Background of the Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness (Paris Declaration)
In recent years, international development objectives such as the MDGs have been collectively set and various efforts are underway with international aid coordination. However, it has become vital to improve the quality of aid as well as increase the volume of aid resources in order to achieve these objectives. Against this backdrop, the Paris Declaration is considered to be a necessary measure for improving the quality of assistance and increasing development results to a maximum by summarizing the partnership commitments for both the aid providing and recipient countries. The Paris Declaration was endorsed at the Second High-Level Forum on Aid Effectiveness, which was held in Paris in March 2005. As of present, 111 countries (including aid providing and recipient countries), 26 multilateral organizations, and 14 private sector groups have endorsed the Declaration. It is widely accepted as a reference for providing high-quality assistance, and it is mainly promoted by the OECD-DAC (Development Co-operation Directorate of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development).
2. Outline of the Paris Declaration
The following items are included in the Paris Declaration.
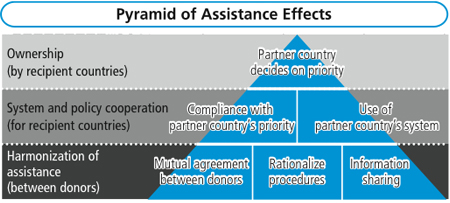
(1) Five key principles for improving aid effectiveness
1) Ownership: Recipient countries exercise leadership in establishing and implementing their national strategies, and aid providing countries and organizations shall support said leadership.
2) Alignment: Donors provide their overall support for the development strategies of recipient countries, and utilize the systems and procedures, such as financial management and procurement, of the recipient country to the highest degree possible.
3) Harmonization: Donors use common systems and procedures whenever possible for assistance planning, implementation, evaluations, and reporting.
4) Managing for Results: Systems in recipient countries for development plans, budgetary measures, and evaluations shall be strengthened, and development results increased by fortifying a mutual relationship of those systems.
5) Mutual Accountability: Donors and recipient countries shall enhance transparency and take mutual responsibility for aid resources, procedures, and development results.
(2) 56 Partnership Commitments
A total of 56 partnership commitments have been accumulated that summarize specific efforts that both donors and recipient countries should make in order to implement the five key principles in a detailed fashion and improve aid effectiveness.
(3) 12 Monitoring Indicators
Twelve indicators have been established, including ratios for assistance provided through co-ordinated programs consistent with a recipient country's national plans, ratios for assistance that use the country's public financial management systems, percentages of aid that are untied, and ratios for surveying and analyses jointly implemented by multiple donors. These indicators shall be monitored.
3. Japan's Efforts
(1) Japan joined in this declaration at the High-Level Forum in Paris while also announcing Japan's Action Plan for Implementing the Paris Declaration. After said announcement, Japan has reported progress of the Action Plan to the OECD-DAC every year.
(2) Japan contributes to promoting the implementation and dissemination of the Paris Declaration centered around Asia, as an aid providing country. In October 2006, Japan co-organized the Asian Regional Forum on Aid Effectiveness in collaboration with the United Kingdom Department for International Development, the Asian Development Bank, and the World Bank. At the forum, information was shared on good practices for cooperative undertakings for harmonization and alignment within Asia. Discussion was held on the importance of ownership and improving the quality of technical cooperation for capacity development in recipient countries, in order to improve the effectiveness of aid.
(3) The Third High-Level Forum on Aid Effectiveness is planned to be held in Ghana in 2008. Japan serves as a member of the forum's steering committee as a major donor, where it takes a leading role in preparations of the forum in order to reflect its past experience in development assistance and good practices in discussion regarding improving aid effectiveness. Most notably, Japan places emphasis, in discussions, on the three issues of capacity development, partnership with emerging donors, and aid effectiveness in infrastructure development.
4. Significance of the Paris Declaration for Japan
(1) The five principles of the Paris Declaration reflect the philosophy of Japan's official development assistance, such as ownership and results-oriented assistance, which derive from the OECD-DAC Development Partnership Strategy that was proposed through the initiative of Japan and endorsed in 1996.
(2) It is necessary to make effort for improving aid effectiveness jointly by Japan and recipient countries in order to effectively utilize limited ODA resources and improve the results of assistance. The Paris Declaration can be utilized as an effective framework for that purpose.


 Next Page
Next Page