Official Development Assistance (ODA)
Cultural Grant Assistance
To promote culture, sports, and higher education in developing countries, as well as provide support for the improvement of facilities and the purchase of equipment to be used in the conservation of cultural heritage, thereby enhancing mutual understanding and friendly relations between Japan and these countries, the Government of Japan provides Cultural Grant Assistance as part of the Official Development Assistance (ODA). The assistance implemented in 2022 consisted of five Cultural Grant Assistance projects (totaling around 503.5 million Japanese yen) and 20 Grant Assistance for Cultural Grassroots Projects (totaling around 169.3 million Japanese yen). In 2022, Cultural Grant Assistance was implemented with an emphasis on the provision of preservation and exhibition equipment for cultural heritage protection facilities, while Grant Assistance for Cultural Grassroots Projects centered on cooperation in promoting sports and Japanese language studies.
I. What is Cultural Grant Assistance?
Cultural Grant Assistance is a scheme whereby funds are granted to cover the cost of procurement, transportation and installation of equipment and construction or restoration of facilities used for various cultural and higher educational activities and the preservation of cultural heritage. From the start of this scheme in FY 1975 to FY 2022, Japan's Cultural Grant Assistance has supported a total of 1,450 projects, disbursing 70.7 billion yen. The equipment and facilities provided to developing countries through Cultural Grant Assistance are used in a wide range of activities, including Japanese-language study and the study of Japan at various colleges and universities; promotion of sports, such as traditional Japanese martial arts like judo, etc.
Some examples of specific projects:
- The Project for the Improvement of Digitization Equipment of the National Library (Moldova)
 (43.7 million yen)
(43.7 million yen) - The Project for the Improvement of TV Program Production Equipment of Cameroon Radio Television
 (145 million yen)
(145 million yen) - The Project for the Improvement of Exhibition Equipment in the National Museum of Iran (approx. 95 million yen)
- The Project for the Construction of the Petra Museum (PDF)

Eligible Countries
Countries eligible for Cultural Grant Assistance are selected from ODA eligible countries and regions specified by the DAC list of ODA recipients.
Eligible Recipients
As aid is provided in the form of grants for the governments of recipient countries, recipients are national government agencies of recipient countries.
Application Process
The organization acting as the liaison for the recipient country (for example, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs) must formulate target projects for that country and make a comprehensive application to the Embassy of Japan or the JICA overseas office.
For more information of Cultural Grant Assistance of Japan (PDF) 
II. What Is Grant assistance for Cultural Grassroots Projects (GCGP)?
Objectives
Grant assistance for Cultural Grassroots Project (GCGP) is meant to facilitate cultural exchanges and deepen friendship and mutual understanding between Japan and developing countries by providing non-profit organizations of those countries with support for procurement of equipment and construction of facilities to promote culture and higher education.
Eligible Recipients
The eligible recipients of GCGP are any type of non-profit organizations which are active at the grass-roots level in developing countries. These organizations include non-governmental organizations (NGOs), local authorities, research and higher education institutions. Under certain conditions, governmental institutions may also be eligible for assistance. Individuals and profit-making organizations are not eligible for GCGP.
Priority areas of GCGP
- Development projects with the main objective of promoting culture and higher education
- Projects with high benefits to the people of the target region
- Projects that contribute to the preservation of the culture of the target region or promote Japanese culture and cultural exchange with Japan
- Projects that contribute to understanding of Japan and foster a sense of affinity toward Japan, and that are easily recognized as development cooperation by Japan
The following types of projects will not be eligible.
- The projects that do not contribute to the economic and social development
- The projects which do not benefit people at the grass-roots level
- The projects that are intended for political or religious purposes
- The projects that could be intended for military purpose
- The projects which include the provision of luxury articles such as alcoholic beverages and cigarette
Available Funds and Implementation Period
The grant amount per project, in principle, is up to 10 million yen. The implementation period of the project is one year after the signing date of the grant contract.
Eligible Countries
Countries eligible for GCGP are selected from ODA eligible countries and regions specified by the DAC list of ODA recipients.
How to Apply
If your organization satisfies the conditions described above and you want to receive GCGP funds in order to implement a project for the promotion of culture or higher education in your country, you should submit an application form to the Japanese embassy or consulate in the said eligible country. The application form must be accompanied by a detailed breakdown of the budget for the project, a map showing the project site, a feasibility study for the project, estimates for the goods and services that will be purchased by the grant (from three different suppliers), the document introducing your organization (such as brochures), its regulations, and the annual budget of your organization.
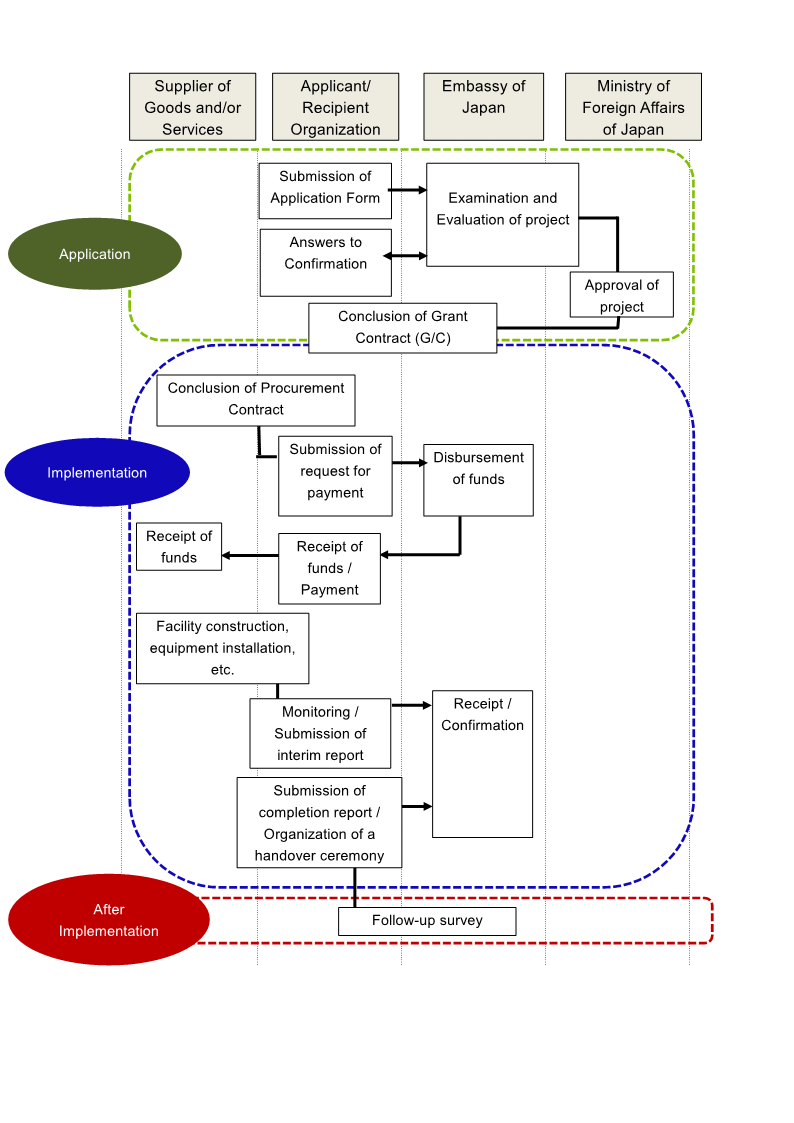
Flow Chart of GCGP
When submitting your application form, please note the following points:
- (1) In selecting projects for funding, the Japanese Government places a high priority on the impact and sustainability of the project. You must convince the Japanese embassy or consulate that your organization can manage the project well. A detailed description of the past achievements of your organization will therefore be helpful.
- (2) The Japanese Government cannot provide funds for salaries and other operating expenses. The operating expenses from the implementation of the project shall therefore be independently financed by your organization. In order to convince the embassy that you can manage the project well, you must show that your organization has sufficient funds to cover running expense.
- (3) Pro forma estimates must be submitted for each budget item so that the embassy or consulate can ensure value for money of the project. Whenever possible, you should submit estimates from three different suppliers.
Approval Procedures
The Japanese Government cannot support every project that is submitted. Funds are provided to appropriate projects after detailed examination and evaluation by the Japanese Government.
After a Japanese embassy or consulate receives an application form and accompanying documents from an applying organization, the embassy or consulate will take the following steps:
- (1) Examination of the project: When the application is received, the project is examined by embassy or consulate staff, who pay particular attention to the objectives, impact, and the cost of the project. On this basis, potential projects for grant assistance are selected.
- (2) Site visit: The embassy (or consulate) staff will visit the site of the potential project.
- (3) Approval of the project: The embassy (or consulate) will send an application of the potential project to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Tokyo, and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs will conduct further examination and approve the project.
- (4) Grant Contract: The Japanese embassy (or consulate) and the recipient organization will then sign a Grant Contract. The Grant Contract contains the title and objectives of the project, the name of the recipient organization, the rights and obligations of each party, the maximum amount that will be provided for the implementation of the project, the submission date of interim/final reports, and the completion date of the project.
- (5) Disbursement of funds: The recipient organization must submit a request for payment with the relevant documents in order to receive the funds.
- (6) Implementation of the project: The grant should be used properly and exclusively for the purchase of the products and/or services specified in the application form of the approved project. Once the grant funds have been disbursed, implementation of the project is expected to proceed in a timely manner and in conformity with the agreed-upon timetable (in principle, within one year).
- (7) Changes from the original plan: If the recipient organization needs to modify the project plan for any reason, it must consult with the embassy (or consulate) and seek its prior approval (both the consultation and approval must be in written form).
- (8) Reports: An interim report during implementation and a final report at the end of the project period are required (in certain cases, the recipient organization may be asked to submit additional interim reports).
- (9) Auditing: External auditing is required for all grass-roots grant assistance above 3 million yen.
Miscellaneous Requirements
- (1) Prospective applicants should note that the following budget items cannot be financed: consumables, operating and maintenance costs of facilities and equipment, administrative costs of the recipient organization, the cost of accepting experts and training, the cost of hosting events.
- (2) Funds received must be used exclusively for the implementation of the project. The Japanese embassy or consulate reserves the right to claim a refund of the grant if the funds are used for any purpose other than for the implementation of the project.
- (3) It would be preferable if the recipient organization could manage the funds for the project separately, such as by opening an exclusive bank account, in order to facilitate auditing of the grant.
For further information please contact a Japanese embassy or consulate.

 )
)