The Hague Convention (Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction)
Assistance in Child’s Return to Foreign State
1 Before filing an application:Be aware of reasons for dismissal.
In case you have a child of yours removed from a Contracting State of the Hague Convention (officially Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction) to Japan , or have a child residing in another Contracting State retained [Note1] in Japan, and want to have the child returned to the state of his or her habitual residence from Japan, you can file an application to the Central Authority of Japan for assistance in order to realize the return of the child to the state of his or her habitual residence (Assistance in Child’s Return to Foreign State).
Your application, however, is to be dismissed if any of the following conditions are met . (Article No.7, Paragraph (1) Implementation Act; officially Act for Implementation of Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction). Therefore, you are advised to make sure that your case does not fall under any of the following items for dismissal.
- The child pertaining to the application has attained the age of 16.
- It is obvious that the child pertaining to the application is not located in Japan and the state or territory where the child pertaining to the application is located is unknown
- It is obvious that the child pertaining to the application is located in a state or territory other than Contracting State.
- It is obvious that the location of the child pertaining to the application and the domicile or residence (or the location of the office if the applicant is a juridical person or other entity) of the applicant are in the same Contracting State.
- At the time of the removal or the commencement of the retention of the child pertaining to the application, the state of habitual residence of said child is not a Contracting State. [Note 2]
- It is obvious that the applicant does not have the rights of custody with respect to the child pertaining to the application under the laws and regulations of the state of habitual residence of said child or that said rights of custody are not breached by the removal or retention of the child pertaining to the application.
[Note1] "Retained" means the condition where a child is prevented from returning to the state of his or her habitual residence after a child travels from the state of his or her habitual residence to Japan and the limited period agreed by both parents passed.
[Note2] Applications are also dismissed if they are concerned with cases of a removal or a retention of the child which began before the enforcement date, April 1, 2014, of both the Hague Convention and Implementation Act in Japan since such cases meet this condition.
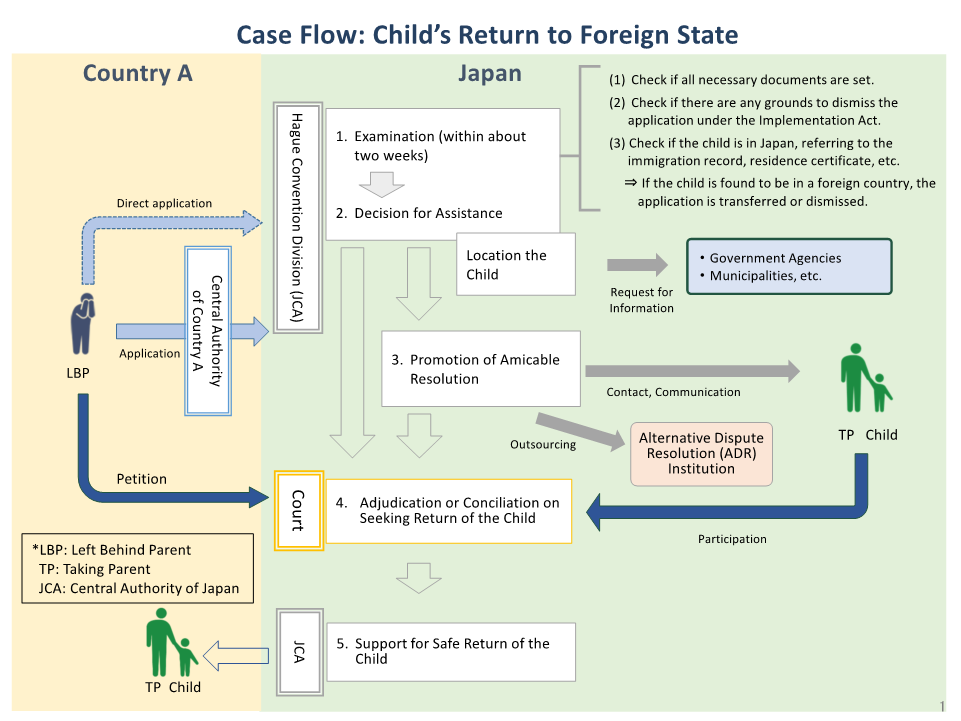
2 Outline of procedures
The outline of the procedures for cases relating to return of child based on the Hague Convention is shown in the below diagram for those who have a child removed from another Contracting State to Japan or who resided in another Contracting State retained in Japan.
3 How to file an application
You can file an application to the Central Authority of Japan for the return of the child following the procedures below.
To file an application for assistance to realize the return of the child to a foreign state (Assistance in Child’s Return to Foreign State) to the Central Authority of Japan, please fill out an application form designated by the Central Authority of Japan and submit it with supporting documents. For more details on required documents and submission method please refer to this page.
[Note] If you wish to take your case directly to court proceedings for the return of the child, you may file a petition to the court without receiving assistance from the Central Authority. For information on petition procedures, please contact directly a family court in Japan or legal professionals. The family courts in Japan, however, cannot respond in languages other than Japanese.
4 Procedures of the Central Authority of Japan upon acceptance of application(The description below, including procedures of the court, only applies to the cases which the Central Authority of Japan made a decision for assistance in child’s return to foreign state.)
(1)Discovery of whereabouts of the child etc.
When the whereabouts of the child pertaining to the application or the person who lives together with the child, is not discovered, the Central Authority of Japan will work to locate the whereabouts of the child and the person who lives together with the child in Japan in cooperation with Governmental Administrative Institutions and Local Governments.
(2)Decision for assistance in child’s return to foreign state
The Central Authority of Japan will first screen the application based on Implementation Act, secondly make a judgment on whether the Central Authority provides the assistance, and then proceed to one of the steps below, and finally notify the applicant of the result.
- Decision for assistance in child’s return to foreign state
- Dismissal of application for assistance in child’s return to foreign state
- Where it is obvious that the child pertaining to the application is located in a Contracting State other than Japan, we will send a copy of the application form and a copy of the attached documents to the Central Authority of the Contracting State.
(3)Service of the Central Authority after Decision for assistance in child’s return to foreign state
Since it is desirable, under the Convention, to make solutions based on an agreement between the parties, the Central Authority provides support such as liaising and coordinating between the applicant and a party preventing return of a child, introducing Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) institutions, and informing the parties of Lawyer Referral Service, if relevant parties want support for mediation.
5 Court Proceedings of Case Seeking Return of Child
If you have a child removed to Japan or retained in Japan, you may file a petition for the return for the child either to Tokyo Family Court or to Osaka Family Court, separately from the application of assistance to the Central Authority of Japan. The petitioner may file a petition for Ne Exeat Order or Passport Surrender Order for the child as a measure to prevent the parent who removed the child from taking him or her out of Japan. (If you want to file a petition for the return of the child, refer to this page. If you want to have conciliation on petition for the return of the child, refer to this page.)
6 Upon the decision to assist in return of child to the state of his or her habitual residence.
When the court decides upon the return of the child, the Central Authority provides support for the child to return safely to the state of his or her habitual residence. (For example, advising on local living support, protection, welfare, indirectly supporting for visa application, and consultation by Japanese embassies on consulate generals after the return of a child)

