Diplomatic Bluebook 2016
Chapter 4
Japan’s Diplomacy Open to the Public
2.Strengthening Foreign Policy Implementation Structure
While the security environment surrounding Japan is increasingly severe, and diplomatic challenges are diversifying, Japan’s foreign policy implementation structure is less sufficient than that of other major countries. As the host country of Tokyo 2020 Olympic and Paralympic Games, it is necessary to enhance the foreign policy implementation structure so that it will be equivalent to that of major countries. In view of this, MOFA is devoted to enhancing its foreign policy implementation structure by reforming the personnel structure and diplomatic missions overseas.
Diplomatic missions overseas, such as Embassies and Consulate-Generals, not only represent Japan but also play a key role in diplomatic areas, such as information gathering on the diplomatic frontline, provision of information to the public overseas, promotion of diplomatic relations, and international contribution. At the same time, they are also responsible for operations directly related to the improvement of benefits for Japanese nationals, such as protecting their lives and safety, providing support for Japanese companies, promoting investment and tourism, and securing energy and other resources.
In January 2016, Japan established Embassies in six countries: the Maldives, the Solomon Islands, Barbados, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Moldova. The establishment of Embassies in these six countries is significant for Japan in terms of the following viewpoints.
As for the Maldives, about 40,000 Japanese people visit the country every year. As located on the Indian Ocean sea lane, it has geo-political importance. The Maldives is friendly to Japan, providing consistent support in the international arena.
The Solomon Islands are bestowed with marine resources such as tuna, as well as mineral resources. In addition, it is necessary for Japan to further strengthen the implementation structure for the Recovery and Repatriation of the Remains of Japanese War Dead.
Barbados is located at an important hub of regional transportation in the East Caribbean area. It is also important for Japan for the purpose of further strengthening relations with major countries of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM), which possess an influence, and have a similar stance with Japan in the international arena.
Tajikistan has a long border with Afghanistan, and thus the country is important in terms of anti-terrorist and anti-drug measures, as well as in contributing to the stability of the entirety of Central Asia. Japan has friendly relations with Tajikistan, a trustworthy country in the international arena.
Turkmenistan is a resource-rich country with the world’s fourth-largest reserves of natural gas. Japanese companies participate in a development project with a total investment of 18 billion US dollars. It is also important for regional stability since the country shares borders with Afghanistan and Iran.
Moldova is located at a point of strategic importance between the EU and Russia, and has been working on democratization and market-oriented economic reform. The country is also important from the perspective of keeping a close watch on the regional situation.
Since the need for supporting Japanese companies is increasing rapidly and provision of information to the public overseas in other cities in addition to capitals is needed, Japan established Consulate-Generals in León (Mexico) and Hamburg (Germany) in January 2016. The Consulate-General in León has jurisdiction over the Bajío region, where many Japanese companies mainly in the automobile industry have started business and the number of Japanese nationals has been increasing rapidly in recent years. In Hamburg, the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea (ITLOS), which plays increasingly important role for the peaceful settlement of maritime disputes in recent years, has its seat. Also, some of German prominent media companies have the headquarters in Hamburg.
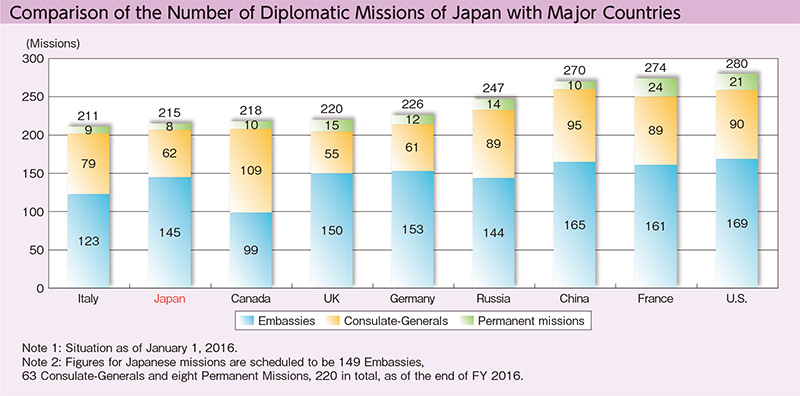
As of FY2015, the number of the diplomatic missions overseas is 215 (145 Embassies, 62 Consulate-Generals and 8 Permanent Missions). The number is still fewer than that of other major countries such as the U.S. (280) and China (270).
In FY2016, based on the idea that it is essential to further strengthen the foreign policy implementation structure, Japan will establish Embassies in four countries: Samoa, Albania, the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYROM), and Mauritius.
Samoa has the largest population in the Polynesian region and is one of the major countries in the region. Samoa has secretariats or regional offices for international organizations: the Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN (FAO), and the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). Samoa is important as the center of information gathering and disseminating communication in the region and for its sea-lane location.
Albania is the base for Albanians, who widely live in the southern part of the West Balkans (The total population of Albanians in the region is about 6 million). Albania has an important role on the stability and development of the region. The strong impact of Albanian immigrants (about 3.5 million) on Europe and the U.S. and rich mineral resources also give significance to the country.
After independence, the FYROM continues reform efforts, aiming at joining the EU and the NATO. Strengthening the relationship with the FYROM is important for Japan in order to strengthen relations with EU and NATO and information gathering on the EU and the Balkan regions, etc. Japan is one of the biggest donor countries to the FYROM.
Mauritius is a stable democratic country with a good business environment. In the future, it is assumed that the country will attract information and people from abroad as a relay point for investments in Africa. There is a potential for Japanese economic activities.
Japan also plans to establish a Consulate-General in Bengaluru, which is a center for the rapidly growing IT industry in India. The number of Japanese nationals and companies in the city has sharply increased.
The current terrorism-related situation is very severe. In recent years, Japanese became victims of terrorism in Syria and Tunisia, etc. ISIL named Japan as one of its targets. Meanwhile, the November 2015 Paris attacks also occurred. Based on a fact that the threat of terrorism against Japan is real, a “Counter Terrorism Unit - Japan” was launched in December 2015 so that the Government of Japan, as a team with the Prime Minister’s Office as headquarters, can promote efforts to strengthen international counter-terrorism measures, including information gathering.
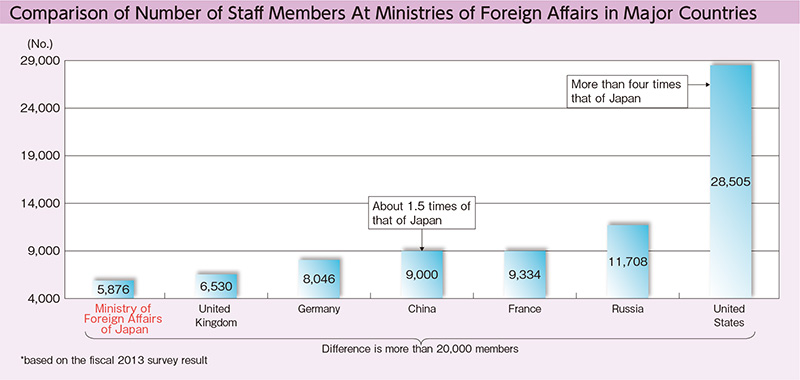
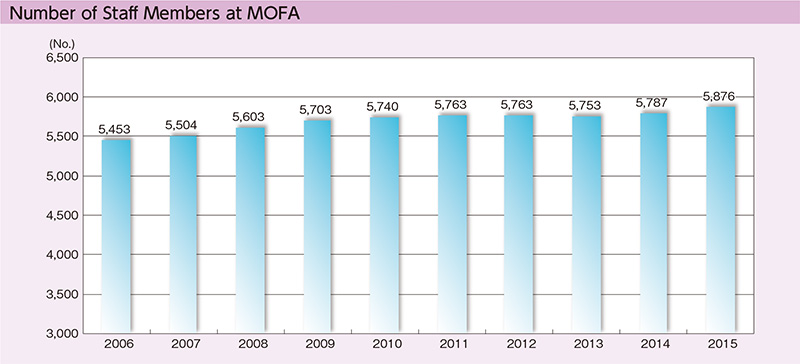
As for the number of staff members, given the government’s policy to reduce the overall personnel expenses across all ministries in the light of the current severe budget situation, MOFA set the number of staff members to be 5,876 in consideration of the importance of strengthening the foreign policy implementation structure including the implementation of “Japan’s foreign policy that takes a panoramic perspective of the world map” and the promotion of economic diplomacy. This number, however, is still insufficient when compared to that of other major countries. MOFA continues efforts to build a structure suitable for our national power and diplomatic policy. In the meantime, based on the understanding that enhancing the foreign policy implementation structure remains necessary in FY2016, MOFA plans to increase its staff members by 90 persons in order to address important issues such as bolstering safety measures for Japanese nationals overseas and strengthening the functions for gathering terror-related information, further expansion of the “Proactive Contribution to Peace” initiative, and promotion of economic diplomacy and supporting the overseas activities of Japanese nationals, as well as strategic provision of information.
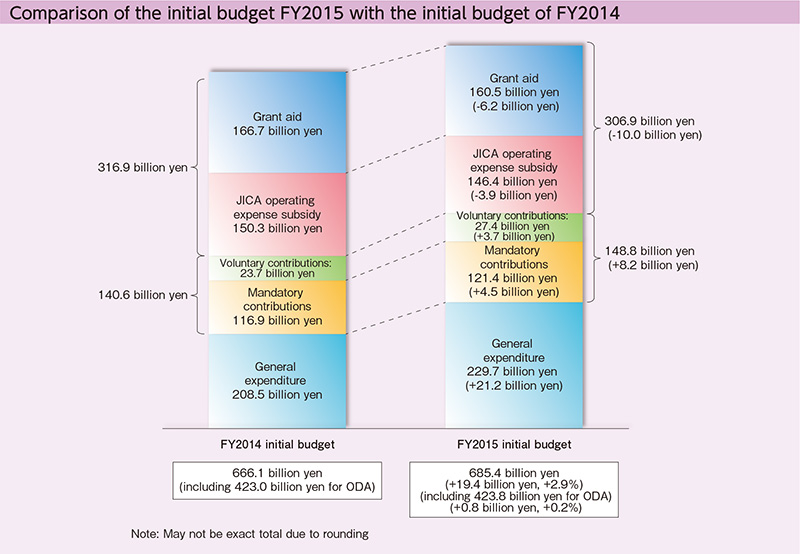
MOFA appropriated a budget of 685.4 billion yen in the budget for FY2015 (an increase of 2.9% from FY2014) to support the foreign policy implementation structure and further strengthen the “Japan’s foreign policy that takes a panoramic perspective of the world map” under “Proactive Contribution to Peace” based on the principle of international cooperation. The total amount of MOFA’s FY2015 supplementary budget was 209.5 billion yen. The budget totaling 186.6 billion yen was allocated as additional financial demand for humanitarian/ counter-terrorism/ society stabilization assistance, including measures to solve refugee issues, and support for responses to global issues including natural disasters and wide-area infections. In addition, a total of 22.9 billion yen is allocated for TPP related measures such as developing the system for the international economic dispute resolution and extending support for overseas operation of Japanese companies and local governments through the use of ODA. By identifying the following key issues and to significantly strengthen the foreign policy implementation structure and dramatically expand ODA to undertake such issues, MOFA’s FY2016 initial government budget proposal appropriated 714 billion yen (an increase of 4.2% from FY2015): (1) bolstering safety measures for Japanese nationals overseas/ strengthening information gathering functions, (2) strategic communication, (3) contribution to global issues based on the policy of “Proactive Contribution to Peace,” and (4) economic diplomacy/ regional vitalization.
In order to promote Japan’s national interests, it is essential to strengthen the foreign policy implementation structure. We will strategically continue to proceed enhancement of foreign policy implementation structure, so that it will be equivalent to that of other major countries, while further streamline the structure itself.