Diplomatic Bluebook 2016
Chapter 2
Japan’s Foreign Policy that Takes a Panoramic Perspective of the World Map
1.Iraq
Following the end of the military operation in Iraq in 2003, Iraq has been working on the new nation-building. At the same time, the Government of Iraq put the priority on fighting against terrorism, realizing the national reconciliation among all domestic parties, and handling of financial difficulty due to the drop in oil prices.
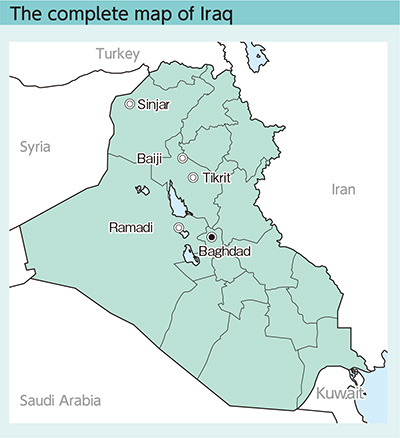
The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) has occupied some areas in the northern and western parts of Iraq. The Abadi administration continued to fight against ISIL and recaptured Tikrit over March and April, while ISIL seized control of Ramadi in May. The fight against ISIL continued a seesaw battle. However, in the latter half of 2015, the Government of Iraq recaptured Baiji at the end of October, and the military units, mainly Peshmerga forces, liberated Sinjar in November. The Government of Iraq has advanced its operations for sweeping ISIL such as regaining control of Ramadi in February 2016.
Prime Minister Abadi intends to work on elimination of the dispute among religious sects and ethnic groups that, in part, triggered ISIL’s aggression, hence to promote reconciliation among all domestic parties. Nevertheless, national reconciliation efforts have not delivered a notable achievement at the national level, as indicating the fact that enactment of the important bills such as national guard bill to promote the establishment of so-called Sunni security forces, is postponed. In order to respond to answer the call the Iraqi people and to garner support to the administration, Prime Minister Abadi issued a Prime Minister’s decree in August regarding the reforms in areas such fields as administration and fiscal management. The purpose of this decree is to ensure prosecution and inspection of these personnel involved in corruption, and streamline government function by integrating and abolishing government organizations. However, it will take time for the reforms to be actually implemented.
Iraq is an oil-based economy with approximately 90% of its annual revenue depending on oil. The drop in oil prices and enormous costs of fight against ISIL posed to serious financial difficulties to causing disruptions of its basic administrative services, such as electricity and water. Under the economic structure heavily dependent on oil revenue, however, the government has yet to work out effective counter-measures.
Japan has been maintaining and strengthening a good relationship with Iraq after the end of the military operation in Iraq in 2003. From February to March, Parliamentary Vice-Minister for Foreign Affairs Sonoura visited Baghdad, Basra, and Erbil to exchange views with government officials, and explained Japan’s unwavering support for Iraq’s fight against extremism.
In October, members of the Japan-Iraq Parliamentary Friendship Association (Chairperson Yuriko Koike: member of the House of Representatives) visited Bagdad when they met Iraqi lawmakers and government officials to enhancement of Parliamentary exchanges between the two countries. Furthermore, in November, the 6th Japan-Iraq Knowledge-Sharing Seminar was held with the aim of promoting reconciliation and rehabilitation in Iraq. Six Iraqi parliamentary members who were from different religious sects were invited. Japan’s experiences of democratization, peace and reconstruction has been shared with the members through the visits to Kyoto and Hiroshima in addition to the talks with government high-level official.
 Parliamentary Vice-Minister for Foreign Affairs Sonoura, visiting a refugee camp at Baharka in the suburbs of Erbil and talking with internally displaced persons (March 15, Iraq)
Parliamentary Vice-Minister for Foreign Affairs Sonoura, visiting a refugee camp at Baharka in the suburbs of Erbil and talking with internally displaced persons (March 15, Iraq)In November, Iraqi Foreign Minister Ibrahim Al-Jafari visited Japan and had a meeting with Japanese Foreign Minister Kishida. The two ministers candidly exchanged their views regarding the fight against ISIL, Syria and regional affairs. Foreign Minister Kishida stated that Japan will support the Government of Iraq, which stands on the front lines of the fight against terrorism and strives to move steadily toward national reconciliation and domestic reforms. He also expressed that Japan will continue to support Iraq in areas including of humanitarian assistance, nation-building and human resource development.
