4. Middle East and North Africa
The Middle East and North Africa region is a major supplier of energy resources, and accounts for approximately 50% of the world's oil and natural gas reserves. In addition, Japan depends on this region for more than 80% of its crude oil imports, and the core maritime route for commerce between Japan and Europe pass through the region. Thus, this region is critical for Japan's economy and energy security.
The Middle East and North Africa region has experienced major political upheaval since 2011. The democratization process is proceeding in the countries where longstanding regimes collapsed. Encouraging reform efforts in such countries through economic assistance and human resources development, etc. leads to peace and stability, not only in these countries and their neighbors, but also in the entire world.
However, this area is facing various challenges that destabilize the region, such as violent extremism including Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), large numbers of refugees, the Syrian crisis, continued tense relations between Gulf countries, tensions in the north of Iraq, the Middle East Peace Process, and the domestic situations in Afghanistan, Yemen and Libya. In 2014, ISIL unilaterally declared the establishment of a self-proclaimed “state” which extends across the national borders of Iraq and Syria. With support from the Global Coalition to Counter ISIL led mainly by the United States as well as other efforts, the Government of Iraq declared the liberation of Mosul, which had been an important base for ISIL, in July 2017. In October the same year, the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) also declared the liberation of Raqqa, which ISIL had claimed as its “capital,” and the area controlled by ISIL has shrunk remarkably. However, threats remain in the form of “lone-wolf” terrorism; therefore it is a significant challenge for the international community as a whole to continuously tackle the fundamental causes behind the growth of violent extremism including ISIL.
Moreover, it is the feature of this region that there are many countries with large youth populations, and it is important to provide support to these countries so that they can continue to achieve stable growth. Realizing peace and stability in this region facing these kinds of issues is extremely important for the international community as a whole including Japan; therefore the international community is working towards the solution of these issues.
<Japan's Efforts>
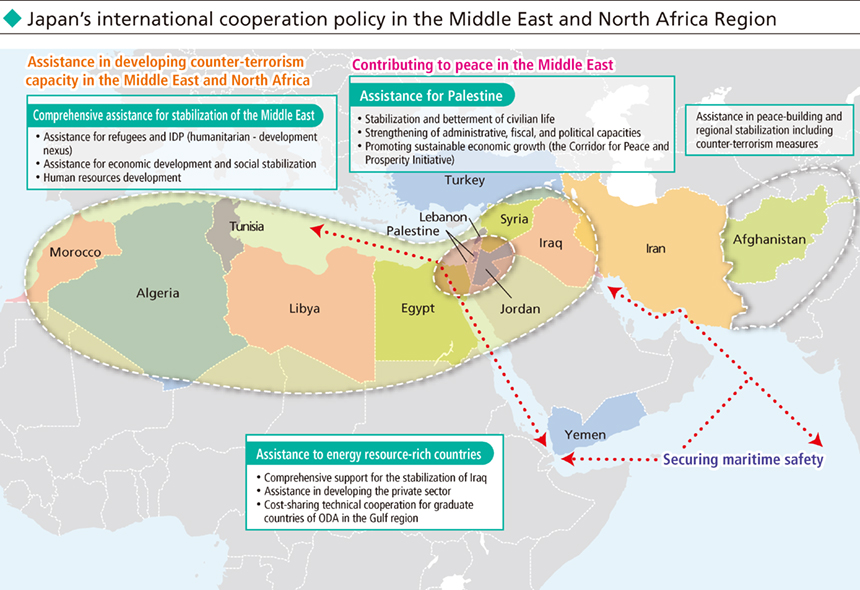
In the Middle East and North Africa, there are many countries and regions with devastated living and social infrastructure and security problems such as Palestine, Afghanistan, Syria, Iraq, Yemen, and Libya. Since peace and stability in these countries and regions have a major impact on the stability and prosperity of the region and the international community as a whole, it is important for the international community to continue to work in solidarity to support these countries and regions for the achievement of sustainable peace and stability, nation-building, and national reconstruction. In view of such characteristics of the Middle East and North Africa regions, Japan's proactive assistance in these regions is of great significance.
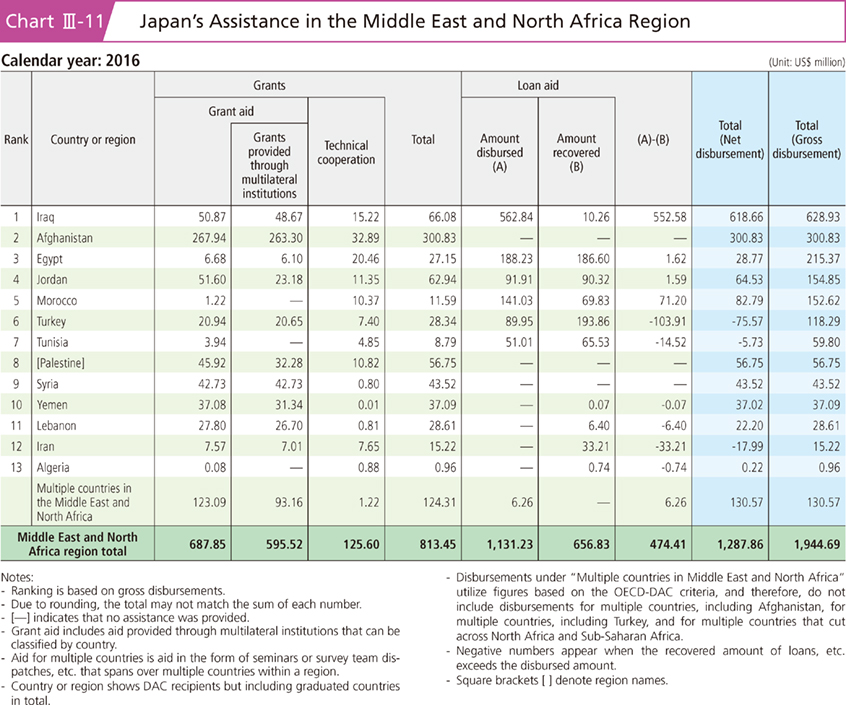
For example, with regard to the Syria issue, which is a pressing concern for the international community, Japan announced the provision of additional assistance totaling $260 million to address the humanitarian crisis, at the Brussels Conference on Supporting the Future of Syria and the Region, held in Brussels in April 2017. In view of the urgency of the situation, this assistance was implemented swiftly. The assistance covers support for displaced persons and the recovery of power supplies as well as the human resources development of youths and the empowerment of women, in order to address the urgent humanitarian need in the region. After the outbreak of the Syrian crisis in 2011, Japan's assistance to Syria, Iraq, and the neighboring countries has exceeded $1.9 billion. In Syria, amidst continuing changes of the humanitarian situation including the declaration of the liberation of ISIL bases in Raqqa and Deir ez-Zor, and the return of IDPs and refugees, Japan provides timely and effective humanitarian assistance.
At the First Japan-Arab Political Dialogue convened in September 2017, Foreign Minister Kono proposed the “Kono Four Principles”(Note 9) as the basic stance for Japan's diplomacy towards the Middle East, and announced five new initiatives(Note 10) as specific proposals towards the realization of the Principles.
Japan will steadily implement the assistance mentioned above and cooperate with the international community to provide not only humanitarian assistance but also support for social stabilization and inclusive growth, including human resources development utilizing the strengths of Japan from a medium- to long-term perspective.
•Egypt
Capacity Development Training for Staffs of Suez Canal Authority
Country-focused training (April 2016 - )
The Suez Canal has supported global logistics and the world economy since it opened in 1869 as the shortest route connecting Europe and Asia without having to detour around the African continent. The Suez Canal collects annual revenue of around $5 billion (2009), which is a significant source of foreign currency income for Egypt (about 10% of the country's overall foreign currency income). However, a number of changes are taking place on worldwide maritime transport, such as the growing size of vessels, the expansion of the Panama Canal, the opening of Arctic shipping routes, and a worldwide downturn in the maritime industry. The changes require that the Suez Canal evolve with the times. To that end, reinforcing the capabilities of the Suez Canal Authority (15,000 employees) operating the Canal has become an urgent task.

Lecture and discussion led by experts
Given these circumstances, Japan held a country-focused training called the Capacity Development Training for personnel of Suez Canal Authority with the goal of enhancing the knowledge and skills needed to properly operate the Suez Canal. This training for employees of the Suez Canal Authority included lectures on, the latest trends in the maritime transport market and site visits to container terminals. The training also consists of analysis and exercises of canal traffic amount prediction modeling and toll setting system in order to improve the necessary practical skills for optimizing income from the Suez Canal.
This training is expected to reinforce the operational structure and capabilities of the Suez Canal Authority and contribute to the sustainable operational management of the Canal. One of those who participated in the training noted that he was able to acquire important knowledge and expertise needed for the future appropriate operation of the Suez Canal.
Japan's cooperation towards the Suez Canal began with ODA loans to fund the construction of the canal's expansion and deepening and procure ships required for the construction, which was essential for the canal to accommodate the growing size of vessels. Since then, Japan has provided continuous assistance to the Suez Canal Authority and has established a strong relationship of mutual trust. Japan plans to continue providing cooperation so that the Canal can adapt to the quickly changing global maritime transport market. (As of December 2017)
- Note 9: (i) Intellectual and human contribution; (ii) investment in “people”; (iii) enduring efforts; and (iv) enhancing political efforts.
- Note 10: The five new initiatives are: (i) upgrading the “Corridor for Peace and Prosperity” initiative; (ii) further contribution to the Multinational Force and Observers: MFO; (iii) expanding cooperation on education and human resources development; (iv) enhancing political efforts; and (v) new humanitarian assistance for refugee and stability.
