Japan's Official Development Assistance White Paper 2011
(1) Assistance to Afghanistan and Pakistan
Continuing unstable situation in Afghanistan and Pakistan is a problem not only for these countries and the surrounding region, but for the entire world as well. The international community, including Japan supports Afghanistan to prevent the country from stepping back to a hotbed for terrorism. The stability of Pakistan, which plays an important role in eradicating terrorism including cleanup operations along the border with Afghanistan, is a key to the peace and stability of the region and the international community.
<Japan's Efforts>
•Afghanistan
Japan has consistently extended assistance to Afghanistan with the total of approximately $3.22 billion since October 2001. In November 2009, Japan announced the "New Strategy to Counter the Threat of Terrorism", and decided to provide assistance up to an amount in the region of $5 billion, in about five years from 2009, based on the future situation of Afghanistan.(Note 18)
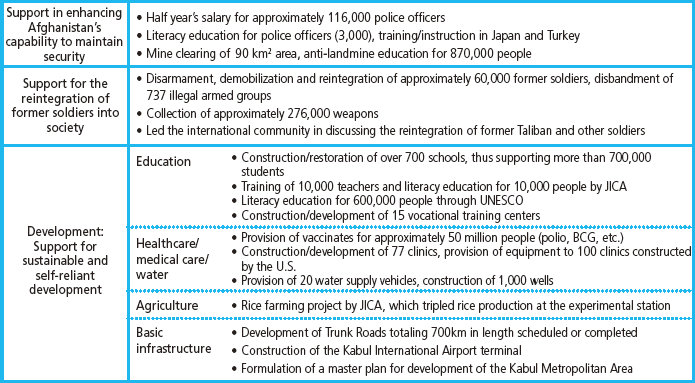
Main areas of Japan's assistance are (i) assistance to enhance Afghanistan's capability to maintain security through such assistance as supporting the Afghan national police, (ii) assistance for the reintegration of former Taliban soldiers through vocational training and development programs for job creation, and (iii) assistance for the sustainable and self-reliant development such areas as literacy and other issues in education, healthcare, agriculture and rural development, and basic infrastructure development (including energy) .
Japan's main disbursements of aid to Afghanistan

Basic coursework at a girl's school as part of the "Strengthening of Teacher Education on Special Education" project (Photo: Raymond Wilkinson/JICA)

Laboratory technicians learn new testing techniques at a hospital as part of the "Tuberculosis Control Project" (Photo: Raymond Wilkinson/JICA)

Painting equipment provided by Japan as part of the "Project for Capacity Development and Establishment of Road Maintenance Management System" (Photo: Raymond Wilkinson/JICA)
•Pakistan
Japan has conducted proactive aid activities since it announced it would implement fight against terrorism in cooperation with the international community following the terrorist attacks in the United States in 2001.(Note 19) Japan formulated its Country Assistance Program in February 2005, and has been active in providing focused on the social sector, infrastructure, agriculture, and the living environment. The Government of Japan and the World Bank co-hosted the Pakistan Donors Conference in Tokyo in April 2009, Japan announced that it would extend up to $1 billion in assistance to Pakistan over the next two years(Note 20). Furthermore, based on the New Strategy to Counter the Threat of Terrorism, issued in November 2009, Japan has steadily provided support exceeding $1 billion for a variety of initiatives for the stable and sustainable development of Pakistan, focusing on assistance for economic growth, macroeconomic reform, improvement of people's livelihood by providing assistance in poverty reduction, and ensuring the stability of people's lives in Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa Province (formerly the North West Frontier Province) and the Federally Administered Tribal Areas(Note 21) (see page 109 for details regarding Pakistan).
Notes:
(18) Replaces the total of approximately $2 billion in aid promised up to this point.
(19) Since in 1998, when Pakistan conducted nuclear tests, Japan has implemented measures to decrease assistance to Pakistan (cessation of provision of new loans and new grant aid excluding emergency humanitarian aid and grassroots grant aid).
(20) Premised on the implementation of an IMF program aimed toward macro-economic stabilization, including economic and financial aspects.
(21) Includes aid for flooding in FY2010.
