Japan's Official Development Assistance White Paper 2010
2. South Asia
The South Asian region includes countries that have high rates of economic growth and gigantic economic potential, particularly India, the world’s largest democracy. Accordingly, this region’s position in the international community is becoming more prominent. South Asia is located on the marine transport route linking East Asia with the Middle East, and thus is strategically important to Japan. It is also an important region from the viewpoint of dealing with global environmental issues. In addition, the region is of great concern to the international community, including Japan, due to the issue of weapons of mass destruction possessed by India and Pakistan and of its role in international undertakings against terrorism and extremism.
However, the South Asian region still faces a large number of issues to be addressed, including a serious lack of basic infrastructure, such as roads, railroads, and ports; growing populations; low school enrollment ratios in primary education; undeveloped water and sanitation facilities along with inadequate healthcare and medical facilities; insufficient maternal and child healthcare; and a lack of countermeasures against infectious diseases and the rule of law. Poverty reduction is a particularly serious issue, where 500 million of the region’s population of 1.5 billion are living in poverty, making it one of the world’s poorest regions. South Asia is the second most important region behind Africa in aiming to achieve the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) (Note 32). For harnessing the economic potential of South Asia and alleviating the widening disparities between the rich and poor, Japan provides assistance to South Asia centered on developing socioeconomic infrastructure.

Parliamentary Vice-Minister for Foreign Affairs Makiko Kikuta visiting the Construction Technology Training Institute (CTTI) in Islamabad, Pakistan
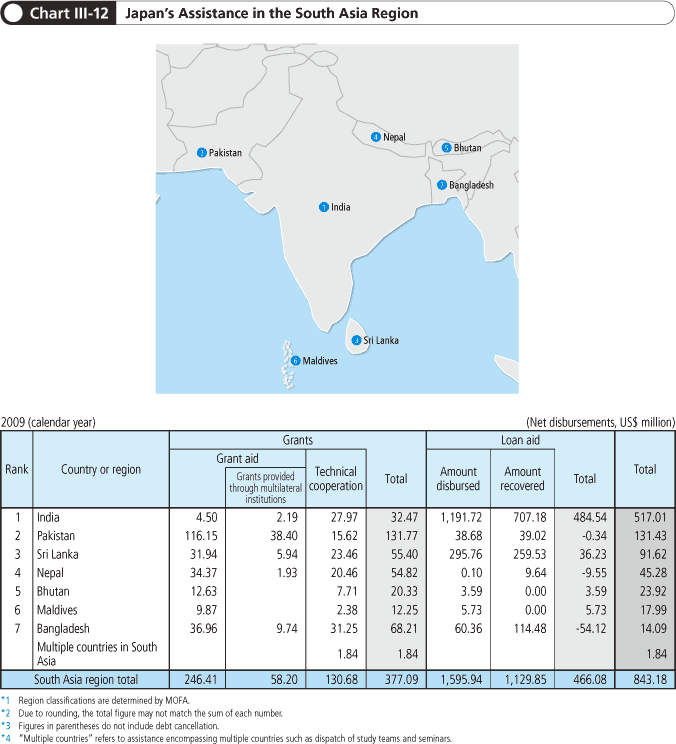
<Japan’s Efforts>
In its relationship with India, a central presence in the region, Japan promotes cooperation in a wide range of fields based on the Strategic and Global Partnership. These include politics and security, the economy, economic cooperation such as the Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) project, the core of the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) project, and academic exchanges. India is the largest recipient country of Japanese ODA loans, and Japan advances the development of economic infrastructure, including power and transport, as well as the development of the social sector aimed at reducing poverty by improving the rural environment.
In May 2009 in Sri Lanka, the more than 25-year battle between government forces and the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) came to an end. Japan provides aid to Sri Lanka while paying consideration to the regional and ethnic balance in order to assist with the promotion of the consolidation of peace and socioeconomic development.
Pakistan plays an important role in undertakings by the international community to eradicate terrorism. The Friends of Democratic Pakistan Ministerial Meeting and Pakistan Donors Conference were held in Tokyo in April 2009. Here Japan announced that it would provide up to US$1 billion in aid to Pakistan, and it has been steadily providing this aid, based on the New Strategy to Counter the Threat of Terrorism, issued in November 2009. Japan provided support to Pakistan, responding to flood damage which occurred in late July 2010 all throughout the country. The support included humanitarian assistance in the form of emergency grant aid, and the dispatch of the Japan Disaster Relief Team composed of a helicopter team of Japan’s Self-Defense Forces (SDF) and of medical teams. At the Pakistan Development Forum in November, Japan newly announced US$500 million of assistance. Japan supports the reconstruction of Pakistan from the flood damage.
●See Part III. Chapter 2. Section 2. 4. Peacebuilding regarding Japan's aid to Pakistan.
In the South Asian region, efforts aimed at aid coordination in various countries are moving forward. With regard to Bangladesh, for instance, in June 2010 the Joint Cooperation Strategy (JCS) was formulated with the participation of 18 countries and organizations, including Japan, the World Bank, the ADB, and the UK’s Department for International Development (DFID). This was done to assist with the implementation of the Second Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper (PRSP-II) (Note 33). Japan is actively working to address aid coordination for Bangladesh, such as by taking part in working committees for the formulation of the JCS.
Notes:
(32) According to the Millennium Development Goals Report 2010, the ratio of people in the South Asian region that live on approximately US$1 a day is 39% (2005). This is the second highest figure behind Sub-Saharan Africa.
(33) Poverty Reduction Strategy Papers are comprehensive and long-term strategies and policies designed to achieve specific reductions in poverty that developing countries draft themselves. In Bangladesh, the Second Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper was formulated in August 2008.
● India: Sikkim Biodiversity Conservation and Forest Management Project
Sikkim State in the northeastern part of India is an extremely important region from the standpoint of conserving biodiversity, as is evident from the fact that nearly one-fourth of all of the plant species found in India inhabit the region. Conversely, in the wake of factors like the sudden rise in the number of tourists in recent years the effects on the natural environment and ecosystems have risen to the forefront. In light of such circumstances, Japan provides assistance for a variety of measures through an ODA loan worth ¥5,384 million. These measures include strengthening the managerial capacity for national parks and protected wildlife preserves located in Sikkim, strengthening and improving the basis for activities of the Sikkim Forest Department, and activities to improve the livelihoods of residents who are dependent on forest resources to make a living. On the basis of the 10th meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP10) to the Convention on Biological Diversity that was held in Nagoya in October 2010, this assistance aims to contribute to environmental conservation and balanced socioeconomic development in India.
