Summary of MOFA ODA Evaluations in FY2024
A total of four third-party evaluations were conducted in FY2024, consisting of one regional assistance evaluation (Regional Evaluation of ASEAN Connectivity Support Centered on the “Japan-ASEAN Connectivity Initiative”), one country assistance evaluation (Evaluation of Japan’s ODA to Nepal), one thematic evaluation (Evaluation of Japan’s COVID-19 Related Cooperation), and one evaluation of individual grant project implemented by MOFA (Japan’s Grant Aid for Economic and Social Development Programme for the Republic of Djibouti in FY2018).
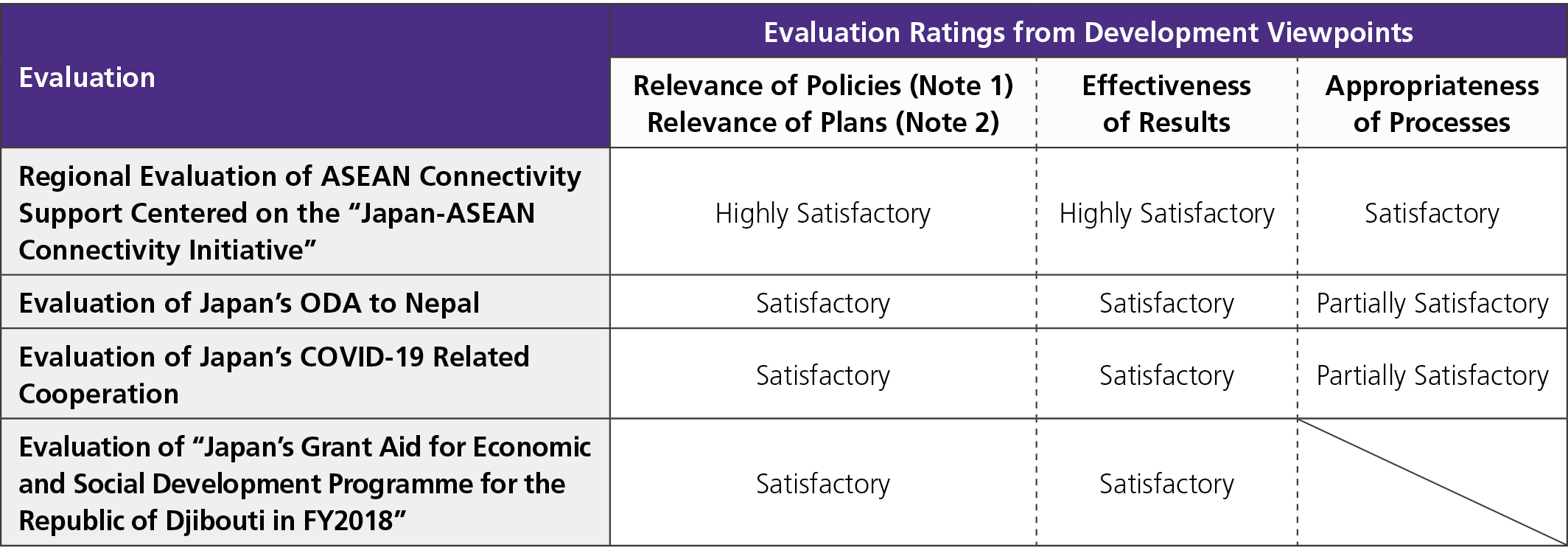
Evaluation from Development Viewpoints
Results of the Policy Level Evaluations (One Regional Assistance Evaluation, One Country Assistance Evaluation, and One Thematic Evaluation)
- Regarding Relevance of Policies, it was confirmed that Japan’s ODA policies for the country and region, and the theme evaluated were aligned with Japan’s high-level policies and the development policies and needs of the partner countries, as well as global priority issues, and that ODA projects were also implemented in a way that leveraged Japan’s comparative advantages.
On the regional evaluation of ASEAN connectivity support, in addition to the aforementioned, ODA policies were consistent with Japan’s foreign policy of a “Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP)” and the priority policies outlined in the Development Cooperation Charter, and it was confirmed that Japan’s comparative advantages, such as comprehensive assistance that effectively combines the physical and non-physical aspects, were verified. Therefore, it was rated “highly satisfactory.” The Evaluation of Japan’s ODA to Nepal and the Evaluation of Japan’s COVID-19 Related Cooperation (thematic evaluation) were rated “satisfactory” for the reasons given at the top of this section. - Regarding Effectiveness of Results, the regional assistance evaluation rated it “highly satisfactory” in view that planned projects are being steadily implemented or have been implemented in the case study countries, alongside the confirmed increase in intra-regional GDP and deepening of international production networks, contribution to long-term human resource development, and benefits to Japanese private companies. In the Evaluation of Japan’s ODA to Nepal, it was confirmed that the inputs for Japan’s assistance were appropriately allocated to priority areas of the country’s needs in line with the Country Development Cooperation Policy and the Rolling Plan, while the expected outputs were achieved. In the thematic evaluation, it was found that wide-ranging cooperation was provided on a global scale, including the provision of vaccines, the development of cold chains, strengthening of testing and epidemic prevention systems, provision of medical equipment, emergency assistance loans, and contributions to international organizations, which provided support in addressing the multifaceted challenges faced by developing countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. Accordingly, both Japan’s ODA to Nepal and COVID-19 related cooperation were rated “satisfactory.”
- Regarding Appropriateness of Processes, in the regional assistance evaluation, processes on the Japan-ASEAN Connectivity Initiative, including policy formulation, implementation, and monitoring, stayed close to ASEAN member countries that value ASEAN connectivity, while continuously contributing to “Quality Infrastructure Investment” in both the physical and non-physical aspects. Thus, it was rated “satisfactory.”
Appropriateness of processes was rated “partially satisfactory” in both the country assistance evaluation and thematic evaluation.
In the country assistance evaluation, it confirmed that various initiatives were implemented for information disclosure and publicity, and that the fine-tuned integration of gender and inclusiveness considerations into various projects led to the promotion of participation and benefits for women and socially vulnerable groups. However, it was pointed out that there were some challenges in the appropriateness of the implementation process of ODA and cooperation policies and in Nepal’s aid implementation system, which involved complex factors.
In the thematic evaluation, it was found that appropriate budgets were allocated to each region and country, and that the generous support provided to Asia, in particular, in light of its economic and diplomatic importance and past cooperation records, contributed to controlling the spread of infections. In addition, success in identifying changing needs through close contacts with local governments and other donors, which made it possible to flexibly address challenges with the existing health care systems and on-site issues, was highly evaluated. On the other hand, delays in procurement caused issues in the provision of equipment for grant projects, and other challenges were identified regarding the simplification of procedures when plans were changed and the publicizing of projects. Thus, it was pointed out that there is a need to promote information sharing among relevant Japanese parties and to improve procedures in cooperation projects with international organizations.
Results of One Evaluation of an Individual Grant Project (Economic and Social Development Programme)
- Regarding Relevance of Plans, this project, which involves rehabilitating a particularly deteriorated section of Djibouti’s National Road 1 (“RN1”), the main artery on the international corridor connecting Djibouti and Addis Ababa, was a top priority issue for Djibouti, and the adoption of modified asphalt in this project was consistent with Japan’s policy of implementing “quality infrastructure” in Africa. Moreover, the change from JICA’s grant to MOFA’s (Economic and Social Development Programme) was an appropriate response that took into consideration the strong desire of the Djibouti side for fast-tracked project implementation. In light of these reasons, relevance of the plan was rated “satisfactory.”
- Regarding Effectiveness of Results, despite overlapping with the COVID-19 pandemic, this project was completed in 18 months. There was a high level of trust in the quality of construction, and the modified asphalt applied at the Japanese section has become the unified quality standard for all sections on the Djibouti side of the Djibouti-Addis Ababa Corridor. Therefore, the effectiveness of the results of this project was rated “satisfactory.”
Rating standards
Highly Satisfactory: All verification items produced highly satisfactory evaluation results.
Satisfactory: Most verification items produced highly satisfactory evaluation results.
Partially Satisfactory: A number of verification items produced highly satisfactory evaluation results, but there were some issues to be resolved.
Unsatisfactory: Most verification items produced unsatisfactory evaluation results.
(Note 1) For policy level evaluations.
(Note 2) For project level evaluations (evaluation for grant projects). Based on the results of the Analysis of Third-Party Evaluation of Bilateral Grant Aid Projects Conducted by MOFA and the Proposal of Evaluation Methods carried out in FY2020, the Development and Diplomatic Viewpoints have been combined since FY2021, and verification items related to “Diplomatic Importance” are included in “Relevance of Plans,” while those related to “Diplomatic Impact” are included in “Effectiveness of Results.”
Evaluation from Diplomatic Viewpoints
In terms of Diplomatic Importance, the regional evaluation mentioned the importance of Japan’s support for ASEAN connectivity with a view to Japan’s national interest, and the “prime water effect” of policy collaboration. In the country assistance evaluation, the geopolitical importance of Japan’s ODA to Nepal was recognized, alongside its importance from the perspectives of securing stability in the Southwest Asian region and maintaining and strengthening good bilateral relations between Japan and Nepal.
In the thematic evaluation, Japan’s COVID-19 related cooperation was highly evaluated for the wide range of assistance provided to low- and middle-income countries to address COVID-19, contributing to the maintenance of global harmony and bilateral relations. It was also appraised for the combination of multilateral cooperation that placed emphasis on equity and bilateral cooperation that made use of strategic approaches, as well as provision of vaccines to Asian countries and assistance to countries where Japanese companies have established operations, which contributed to the recovery of economic activities and the security of the Japanese people.
On Diplomatic Impact, the regional evaluation recognized the “prime water effect” leading to economic impacts such as the expansion of the industrial base, as well as the expansion of exchanges at the governmental, private and civilian levels. The Evaluation of Japan’s ODA to Nepal recognized the significant contribution of Japan’s ODA toward the peace, stability, and prosperity in Nepali society, fostering a broad pro-Japanese sentiment extending from the Government of Nepal to the general public. which has influenced the friendship, exchanges, and movement of people between the two countries.
In the thematic evaluation, Japan’s COVID-19 related cooperation was evaluated for its multifaceted diplomatic impact, including improving Japan’s international presence and credibility, contributing to the strengthening of bilateral relations with various countries around the world, and ensuring the safety of Japanese people and promoting economic reconstruction.
Recommendations and Lessons Learned
Recommendations were made based on the results of the four ODA evaluations conducted in FY2024. Of those recommendations, the following are common to multiple evaluations or applicable to other cases.
Recommendations Common to Multiple Evaluations (Recommendations for Subjects of Evaluation)
● Promotion of wide-area cooperation
Promoting wide-area cooperation was proposed in multiple evaluations. It was also recommended that the focus be placed on supporting multi-country infrastructural development and knowledge assistance (dispatching experts, training, etc.), and to promote cooperation with regional organizations (Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and ASEAN Centre for Public Health Emergencies and Emerging Diseases (ACPHEED)) and strengthen their capabilities. Furthermore, the importance of taking a wide-area perspective in project formulation was pointed out.
● Importance of human resource development
Common recommendations on the importance of human resource development were also made. These included continued support that combined physical (infrastructure development) and non-physical (human resource development) aspects, strategic human resource development and capacity building, and prioritizing the capacity building of emergency responders in healthcare and medical services in developing countries.
Recommendations/Lessons with Possible Applicability to Other Cases
● Cooperation of “physical aspects” and “non-physical aspects” in areas where Japan has a comparative advantage
It was confirmed that Japan’s comparative advantage lies in achieving synergistic effects through cooperation between infrastructure construction and rehabilitation (“physical aspects”), particularly in areas where Japan has a strong comparative advantage, and technical cooperation (“non-physical aspects”) to strengthen systems and build capacity in the areas of operation, maintenance, and management, as well as in providing assistance in ways that combine both “physical” and “non-physical” aspects of assistance.
● More effective publicity
Specific recommendations were made toward ensuring more effective publicity. These include the following: regarding cooperation with international organizations, monitor activities and results and publicize projects in ways that show clearly that they are Japanese ODA projects; strengthen efforts to promote projects in an easy-to-understand manner in the local language, using videos and other means to publicize the benefits that Japan’s ODA projects bring to partner countries; and explain Japan’s support to ASEAN and concepts in ways that are in line with ASEAN’s strategy document.
