

| Part III. | ODA DISBURSEMENTS IN FISCAL YEAR 2002 |
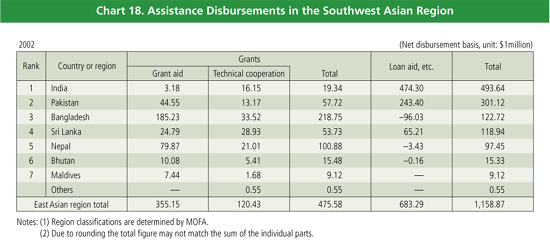
Japan’s bilateral ODA to the Southwest Asian region in 2002
was approximately $1.16 billion, 17.2% of total bilateral ODA.
Japan has been carrying out assistance in the Southwest Asian region placing
importance on the following points, as stated in the medium-term policy.
| (1) | Japan will provide support for alleviating poverty and ensuring the livelihood of the poor (focusing on assistance for BHN, including health and medical services, primary education, and agricultural and rural development, etc.). |
| (2) | Japan will provide support for human resources development and social and economic infrastructure development in order to revitalize private-sector activities and to create a more attractive environment for foreign investment. |
| (3) | Japan will provide support for environmental conservation to cope with the increasing environmental burden created by population and economic growth. |
The Southwest Asian region is home to one-fifth of the world’s
population, many of whom live in poverty, as four countries in the region are
classed as least developed countries (LDCs). In addition to its poverty and
population problems, the Southwest Asian region is also plagued by low rates
of primary school enrollment, inadequate healthcare, and infectious diseases.
Along with Africa, it presents the international community with the greatest
challenges regarding the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).
The Southwest Asian region has become the focus of major concern for the international
community, including Japan, due to the nuclear nonproliferation issue and the
“fight against terrorism” in the wake of the September 11 terrorist
attacks in the United States (US).
It is necessary for Japan to continue to place importance on measures to overcome
the poverty issue faced by this region and to support desirable movements toward
stability and development of the region, for example economic liberalization
of the countries in the region, regional cooperation focused on economic aspects,
etc as well.
As support for alleviating poverty and ensuring the livelihood of the poor,
Japan is coordinating grant aid and technical cooperation to provide cooperation
in the BHN sectors, such as agriculture, living environment, health and medical
services, etc. particularly to LDCs like Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal and the Maldives.
In particular Japan is supporting the World Health Organization (WHO) target
of “eradicating polio from the world by 2005” and in order to achieve
that target, following on from the eradication of polio from the Western Pacific
region, it has been providing active support for the eradication of polio from
the Southwest Asian region. In fiscal year 2002 Japan provided India, Pakistan
and Bangladesh with grant aid through the United Nations Children’s Fund
(UNICEF) for the “Project for the Eradication of Poliomyelitis” of
each of those countries. And in November 2001 Japan announced it would provide
Pakistan with grant aid of $300 million over approximately two years to support
poverty reduction, including support for the education and health sectors. Currently
Japan is providing this assistance.
Looking at support for human resources development and social and economic infrastructure
development intended to revitalize private-sector activities and create a more
attractive environment for foreign investment, because both India and Pakistan
have relatively high technology standards, Japan is providing mainly Nepal,
Bangladesh and Sri Lanka with support for human resources development. Concerning
social and economic infrastructure development, Japan is mostly carrying out
projects related to basic infrastructure through grant aid in the LDCs within
the region. And, Japan is using ODA loans to provide funds for the “Power
Sector Restructuring Program,” the “Rural Economic Development and
Promotion Project,” the “Small-scale Infrastructure Rehabilitation
and Upgrading Project,” etc. as support to contribute to poverty reduction
and reforms in the energy sector and transportation infrastructure sector in
India and the electricity supply sector in Sri Lanka.
Looking at support for environmental conservation to cope with the increasing
environmental burden created by population and economic growth, in fiscal year
2002 Japan implemented the “Punjab Afforestation Project (II)” and
the “Rajasthan Forestry and Biodiversity Conservation Project” with
ODA loans as cooperation for forest conservation in India where environmental
degradation is a particularly serious problem.
Refer to Part I for details about support for
the peace process in Sri Lanka.
 |