

| Part III. | ODA DISBURSEMENTS IN FISCAL YEAR 2002 |
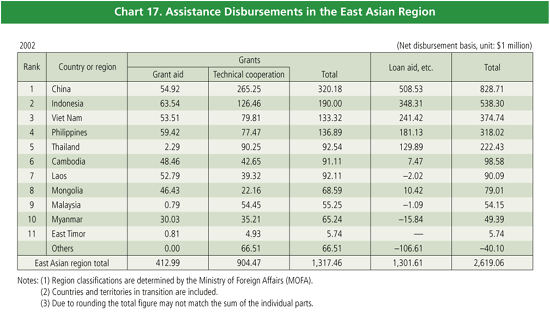
Japan’s bilateral ODA to the East Asian region in 2002 was
approximately $2.62 billion, 39.0% of total bilateral ODA20.
Japan has been carrying out assistance in the East Asian region placing importance
on the following points, as stated in “Japan’s Medium-Term Policy
on ODA” (hereinafter to be referred to as the “medium-term policy”)
formulated in 1999.
| (1) | Japan will provide support for economic structural adjustment to overcome the economic crisis and to achieve economic recovery. |
| (2) | Japan will provide active support to the socially vulnerable to improve their living standards and domestic conditions. |
| (3) | Japan will provide support for human resources development and institutional building to promote the development of supporting industries and appropriate social and economic management. |
| (4) | Japan will provide its assistance to poverty alleviation programs, social and economic infrastructure development, environmental protection, and agricultural and rural development projects in accordance with the needs and conditions of each country. |
| (5) | Japan will provide support for regional development initiatives such as Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) intraregional cooperation, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation’s (APEC) regional cooperation, Mekong basin development and “South-South cooperation.” |
The East Asian region is the region that Japan has traditionally
regarded as the priority region. The revised ODA Charter also designates the
East Asian region, including ASEAN as a priority region. This is because Japan
and the East Asian countries are in a closely interdependent relation in all
aspects including those of policy, economy and culture, etc. and the development
and stability of East Asia are extremely important for the stability and prosperity
of Japan. Based on these concepts, Japan has contributed to the region’s
remarkable development by promoting economic cooperation in which ODA and investment
and trade are organically coordinated. The cooperation includes the dynamization
of private-sector investment and trade through economic infrastructure development,
etc. by using ODA.
East Asia has attained rapid economic growth, and some countries, such as the
Republic of Korea (ROK) and Singapore, have already been transformed from aid
recipients into aid donors. On the other hand, there are still some least developed
countries (LDCs) such as Cambodia and Laos. And there is a movement for Japan
to modify its ODA priority sectors against a background of dramatic economic
growth, etc. in some countries like China. Japan is carrying out assistance
fully taking into account the diversity of the Asian countries’ socio-economic
conditions and changes in their respective assistance needs, etc.
Japan is actively using its ODA to reduce the disparities within ASEAN region,
which are becoming more apparent as membership expands, and to implement cooperation
in sectors such as institution building for the facilitation of trade and investment,
support for economic and social infrastructure development, human resources
development, promotion of environmental conservation, policy formulation for
economic restructuring, decentralization and governance, and measures to deal
with terrorism, piracy and other transnational issues, etc. In pursuing these
tasks Japan is giving careful consideration to enhancing economic partnership,
etc. in East Asia.
In the ASEAN region, Japan is carrying out cooperation based on the development
situation of each country, aiming at the complete recovery of the ASEAN region
from the economic and financial crisis and the reduction of economic disparities
within the region. In particular for less developed countries such as Cambodia,
Laos and Viet Nam, Japan is continuing to provide support for their transition
to a market economy, implement assistance in social development sectors like
poverty reduction and Basic Human Needs (BHN) and also provide support for development
of various economic infrastructures such as roads and electricity grids. Japan
is also actively working on the Mekong Region Development, which contributes
to reducing disparities within the region. (Refer
for details.)
Meanwhile, partly because Japan has continued its support for Indonesia, the
Philippines, Thailand, and Malaysia focusing on the development of economic
and social infrastructure mainly by using ODA loans, the movement of goods,
people-to-people exchanges, flow of information, etc. within the ASEAN region
are becoming smoother.
Furthermore, in addition to bilateral assistance, Japan is
actively promoting South-South cooperation based on cooperation within the ASEAN
region and Partnership Programs*1 with Singapore,
Thailand, and the Philippines from the perspective of strengthening ASEAN integration.
Japan also attaches importance on the promotion of Asia-Africa cooperation.
For example, it is providing support for African countries such as productivity
improvement through third country training.
Concerning Mongolia, Japan has actively supported its democratization and transition
to a market economy and carried out human resources development, etc. Moreover,
Japan decided to provide funds for the “The Project for Improvement of
Shortwave Radio Broadcasting Network” through grant aid believing that
such a project widely benefits the nomadic herdsmen who live throughout the
vast land area of Mongolia and account for the majority of the country’s
population. It is expected that this project will make it possible to widely
provide the people of Mongolia, including the nomadic herdsmen with information
such as information on the national policies of Mongolia and meteorological
and disaster.
Concerning China, Japan is carrying out assistance in accordance with the Economic
Cooperation Program for China formulated in October 2001. The majority of Japan’s
ODA loans to China in fiscal year 2002 was allocated to environmental projects
and their amount declined approximately 25% in monetary value terms from the
previous fiscal year (Exchange of Notes (E/N) basis). (Refer
for details.)
The Initiative for Development in East Asia (IDEA) is one of Japan’s new
efforts. At the first IDEA Ministerial Meeting proposed by Japan and held in
Tokyo in August 2002, Japan, China, ROK, and the ASEAN countries held very meaningful
discussions. For example they frankly exchanged views about the direction of
economic partnership and regional cooperation in the East Asian region. As follow
up to this meeting, Japan held a side event at the World Summit on Sustainable
Development (WSSD) in Johannesburg (the Johannesburg Summit) at the end of August
2002 to present the content of IDEA, and the growth-orientated development modality
of East Asia that relies on the utilization of ODA to promote trade and investment
attracted a lot of attention among officials of African governments. Refer
for details about the Ministerial Meeting.
As cultural cooperation in the East Asian region, in the fields of preservation
and restoration of the Angkor ruins, which is universally admired worldwide,
Japan has been implementing the “Project for the Preservation and Restoration
of the Angkor Monuments” (currently in Phase II) since 1994 through the
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) by
utilizing UNESCO Japanese Trust Fund for the Preservation of the World Cultural
Heritage. Japan is dealing with not only the preservation and restoration of
the ruins, but also the training of the Cambodians. Japan’s assistance
is contributing to the cultural reconstruction of Cambodia and is also highly
appreciated by the international community.
| |
Assistance for Countermeasures against terrorism and the Consolidation of Peace in the East Asian region |
East Asia is an important region from the perspective of eradicating
international terrorist activities. In October 2002 the Bali bombing occurred
in Indonesia, in the Philippines, etc., terrorist incidents are also taking
place and the extension of Islamic extremists’ power is being blamed. Japan
is placing importance on support for countermeasures against terrorism in this
region, and also is cooperating in enhancing these countermeasures through support
for police, provision of equipment, etc. in Indonesia and the Philippines. Furthermore,
Japan is implementing cooperation for poverty reduction in East Asia with a
view to eliminating hotbeds of terrorism.
And various issues requiring the “consolidation of peace” are also
present in the East Asian region, for example the Aceh issue in Indonesia and
the Mindanao issue in the Philippines. Japan is carrying out support for movements
toward peace in these areas. (Refer to Part III
for details.)
 |
20. Disbursements are from
DAC statistics (calendar year). (DAC statistics are also used in the rest of
this section.)