
| Part III. |
ODA DISBURSEMENTS IN FISCAL YEAR 2002 |
Chapter 2
Section 2
8. European Region
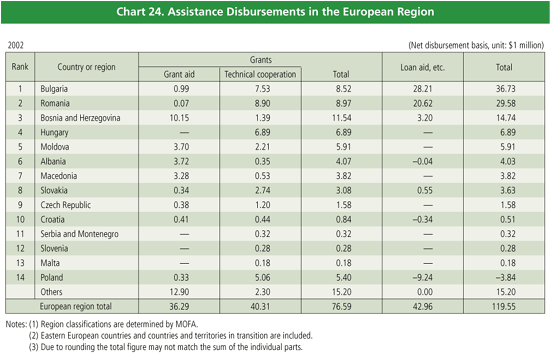
Japan’s bilateral ODA to the European region in 2002 was
approximately $120 million, 1.8% of total bilateral ODA.
Japan has been carrying out assistance in the European region placing importance
on the following points, as stated in the medium-term policy.
| (1) |
Japan will provide support for the transition to a market
economy, for environmental conservation, and for infrastructure restoration
and development. |
| (2) |
Japan will provide humanitarian aid to refugees,
economic and social infrastructure development for the promotion of restoration
and reconstruction, assistance in the area of basic human needs, and support
for the implementation of elections in the former-Yugoslav region and neighboring
countries. |
Japan commenced substantial assistance for the European region
after the collapse of communism in 1989 and is currently providing assistance
to 18 countries in the region. The region was under centrally planned economic
systems for a long period and there are some countries in the region, such as
Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia and Montenegro, etc. that have suffered a lot
of damage through conflicts and require restoration and reconstruction, and
some countries such as Bulgaria, Romania, etc. that require assistance because
they are lagging behind in the transition to market economies. On the other
hand, there are countries such as Poland and Hungary that are well advanced
along the path to democratization and market economies and are due to accede
to the European Union (EU) in 2004. In many countries environmental measures
are being neglected as countries focus on economic growth. Because the pollution
issue has a big impact on neighboring countries too, Japan is aiming for sustainable
development and is pouring its efforts into support for environmental conservation
policies.
As for support to promote the transition to a market economy, for a number of
countries including Croatia, Serbia and Montenegro, Bulgaria, Romania, etc.
Japan is carrying out human resources development through the dispatch of experts
and the acceptance of trainees in order to promote small and medium-sized enterprises,
promote trade and build an investment environment.
In the environmental conservation sector, Japan is carrying out the dispatch
of experts in the prevention of air pollution and water pollution and energy
conservation policy, etc. and in Bosnia-Herzegovina Japan is carrying out development
surveys, etc. concerning the “The Study on Sustainable Development through
Eco-Tourism in Bosnia Herzegovina” project. And from the perspective of
regional cooperation, Japan is dispatching regional experts for the “Sava
River Water Quality Management” project for Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina,
and Serbia and Montenegro.
In the regions of Southeast Europe that were affected by conflicts, such as
the former Yugoslavia, etc., Japan is carrying out humanitarian assistance through
international organizations, primarily the United Nations High Commissioner
for Refugees (UNHCR), etc., and providing grant aid with the objective of restoration
and reconstruction of infrastructure and the BHN sectors in Bosnia and Herzegovina,
Serbia and Montenegro, etc. For Macedonia, Albania, etc. as a part of its support
for poverty reduction, Japan is also implementing grant aid, the acceptance
of trainees studying hospital management, and other measures, all designed to
develop basic infrastructure and establish health and medical services institutions,
which are still inadequate.
On their accession to the EU, ten countries including countries in Central and
Eastern Europe and the three Baltic countries will become donor countries and
in order to support this process, in Poland and Hungary Japan is implementing
“triangle cooperation,” which transfers the know-how accumulated through
previously implemented technical cooperation to third countries. Specifically,
the “Polish-Japanese Institute of Information Technology” and “Hungarian
Productivity Center,” which have carried out dispatches of experts, acceptance
of trainees, provision of equipment, etc. through previous technical cooperation
projects, are used as bases for carrying out third country training in which
trainees are gathered from neighboring countries such as Bulgaria, Romania,
etc. and technology transfer is carried out. This cooperation does not only
support the processes of donor countries; it also contributes to the development
of the entire European region.
| Column 9 |
Japan’s Serbia and Montenegro (Yugoslavia)
Reconstruction Support |
|
In the spring of 1998, clashes occurred between the Kosovo
Liberation Army (KLA), an armed organization of ethnic Albanian residents,
and Serbian security forces and tensions heightened in the Kosovo region.
Subsequently, after the collapse of an attempted peace settlement, on
March 24, 1999 the then Federal Republic of Yugoslavia faced airstrikes
by NATO which was trying to urge Yugoslavia to accept the peace plan.
The country began the transition to democracy after the defeat of the
then President Slobodan Milosevic in the elections in fall 2000. However
the territory of the country was devastated by the conflict, there was
the negative legacy left by the enormous military budget of the Milosevic
administration in the 1990s (more than half of the national finances)
and the economic condition of the country was severe with about a triple-digit
inflation rate. Under the circumstances, Japan officially announced
its resumption of economic cooperation, which had been suspended since
1991, and provided emergency assistance of $10 million, humanitarian
assistance to rescue refugees and agricultural support for Yugoslavia,
which was facing the immediate concern of how to get through the upcoming
winter of 2000. Following on from this, Japan announced assistance of
$50 million at the Consultative Group Meeting for Yugoslavia in June
2001. This assistance has been mainly used in the medical services,
infrastructure development (transportation, electricity supply), and
agricultural sectors, contributing to economic growth and poverty reduction
through the restoration and reconstruction of Serbia and Montenegro.
Most of the citizens of Belgrade use buses as a means of transportation,
however, it was difficult to provide appropriate service because of
aging busses and shortage of available buses. Japan provided 93 buses
through grant aid to the bus routes in Belgrade where bus users are
concentrated and these buses are today active as the “legs”
of the people in Belgrade. In the medical services sector, the serious
shortage of medical equipment is a priority issue in Yugoslavia, therefore,
Japan is implementing cooperation through grant aid including the provision
of diagnostic and emergency medical equipment to four central hospitals
in the region.
In the agricultural sector, in addition to the purchase of fertilizer
implemented through emergency grant aid in 2000, Japan implemented support
for the purchase of large tractors and other support through non-project
grant aid in 2001 and contributed to the agricultural production in
Yugoslavia. According to a Japanese government official at that time,
the major factors contributing to this success were the high capacity
of the Serbia and Montenegro side for implementation and response and
the publicity efforts of the government within the country.
In addition, one of the grant assistance grassroots projects carried
out in collaboration with a Japanese NGO was a project to reconstruct
Albanian and Serbian primary schools and clean the town in regions of
Kosovo where ethnic Albanians and ethnic Serbs were living together.
This project was also effective in establishing order in Kosovo.
Receiving assistance from Japan and the other donor countries, the economic,
financial and fiscal situation in Serbia and Montenegro has been gradually
improving. To date, Japan has mainly carried out restoration and reconstruction
assistance focused on infrastructure development and humanitarian assistance,
but there are still many poor people in the region as a result of ethnic
problems and conflicts between ethnic groups, so currently Japan is
studying ways to provide support that will contribute to the consolidation
of peace and economic development of the country.
 |
| A billboard in Belgrade showing the Japanese ambassador. It was put up after Japan’s assistance was covered on television. (Belgrade City) |
|
 |
Previous Page | Next Page


