
1. Japan's Official Development Assistance (ODA)
Grant Aid
Grant aid is financial assistance that is extended to developing countries without imposing an obligation of repayment. It is classified into two broad categories: General Grant Aid and Grant Aid related to Food and Agriculture.
(1) General Grant Aid
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan examines requests for grants submitted by developing countries and if deemed appropriate, extends grant assistance to a recipient country. The related budget item is included in the Budget for Economic Development Assistance.
(2) Grant Aid related to Food and Agriculture
(i) Food Aid (generally referred to as KR)
Food Aid is provided to developing countries in accordance with the Food Aid Convention of 1995. Japan's minimum annual obligation under the convention is 300,000 tons in wheat-equivalent terms.
(ii) Grant Aid for Increase of Food Production
Grant Aid for Increase of Food Production is extended to developing countries to finance their procurement of agricultural equipment and materials, such as fertilizer, agrochemicals, and agricultural machinery, in order to increase their food self-sufficiency. Japan has been providing this type of aid since 1977.
Technical Cooperation
Technical cooperation is a form of aid that seeks to transfer technology to developing countries, thereby improving technological levels in such countries. Person-to-person contact is the cornerstone of this form of aid. Technical cooperation thus has a characteristic that is absent from the other forms of cooperation; it enhances mutual understanding between the peoples of different nations.
The mechanism for implementation of technical cooperation comprises the formulation of plans and preparation of budget requests by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, followed by the actual implementation by the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
Technical cooperation programs comprise the following activities:
| (i) | | Acceptance of trainees and other personnel,
|
| (ii) | | Dispatch of experts, survey teams, and volunteers from the Japan Overseas Cooperation Volunteers (JOCV),
|
| (iii) | | Provision of equipment and materials associated with the human resources mentioned in (i) and (ii),
|
| (iv) | | Project-type technical cooperation, which encompasses a combination of human, equipment, and material resources for specific project initiatives (social and industrial development, agricultural and forestry industries, health and medical care development).
|
Capital Subscriptions and Contributions to International Organizations
This form of aid comprises indirect assistance given through international organizations.
Unlike bilateral loans, which are direct diplomatic initiatives extended by donor countries to recipients, aid provided through multilateral organizations has the advantage in that political neutrality is guaranteed. It also allows advanced specialist knowledge and experience in each multilateral organization to be harnessed and the resources of the global aid network to be put to greater use.
The mechanism by which this form of aid is implemented is as follows: In accordance with the quotas assigned to Japan, contributions destined for various UN agencies (United Nations Development Programme, United Nations Population Fund , United Nations University, the Colombo Plan, the Asian Productivity Organization, etc.) are chiefly the responsibility of the Ministry for Foreign Affairs, while the Ministry of Finance is chiefly responsible for subscription of equities for multilateral development banks (the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, Inter-American Development Bank, etc.). Each ministry requests the necessary budget amounts to be contributed or to be paid for subscription.
Loan Aid
Loan aid involves the provision of long-term low-interest loans, generally known as ODA loans, to recipient countries. Loan aid accounts for approximately 30% of Japan's ODA expenditure.
ODA loan programs are implemented by the Overseas Economic Cooperation Fund (OECF), under the terms of an agreement between four ministries, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of International Trade and Industry, and the Economic Planning Agency.
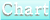 Mechanism for the Provision of General Grant Aid
Mechanism for the Provision of General Grant Aid
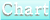 Value of Economic Cooperation Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
Value of Economic Cooperation Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
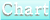 Official Development Assistance Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
Official Development Assistance Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
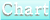 Mechanism of ODA Loan Implementation
Mechanism of ODA Loan Implementation
Back to Index


 Mechanism for the Provision of General Grant Aid
Mechanism for the Provision of General Grant Aid
 Value of Economic Cooperation Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
Value of Economic Cooperation Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
 Official Development Assistance Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
Official Development Assistance Provided by Major Advanced Countries (1996)
 Mechanism of ODA Loan Implementation
Mechanism of ODA Loan Implementation